Effects of activin and TGFβ on p21 in colon cancer
- PMID: 22761777
- PMCID: PMC3383701
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039381
Effects of activin and TGFβ on p21 in colon cancer
Abstract
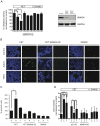
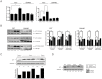
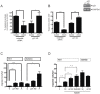
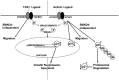
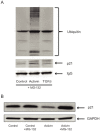
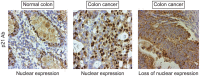
Activin and TGFβ share SMAD signaling and colon cancers can inactivate either pathway alone or simultaneously. The differential effects of activin and TGFβ signaling in colon cancer have not been previously dissected. A key downstream target of TGFβ signaling is the cdk2 inhibitor p21 (p21(cip1/waf1)). Here, we evaluate activin-specific effects on p21 regulation and resulting functions. We find that TGFβ is a more potent inducer of growth suppression, while activin is a more potent inducer of apoptosis. Further, growth suppression and apoptosis by both ligands are dependent on SMAD4. However, activin downregulates p21 protein in a SMAD4-independent fashion in conjunction with increased ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation to enhance migration, while TGFβ upregulates p21 in a SMAD4-dependent fashion to affect growth arrest. Activin-induced growth suppression and cell death are dependent on p21, while activin-induced migration is counteracted by p21. Further, primary colon cancers show differential p21 expression consistent with their ACVR2/TGFBR2 receptor status. In summary, we report p21 as a differentially affected activin/TGFβ target and mediator of ligand-specific functions in colon cancer, which may be exploited for future risk stratification and therapeutic intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Chen YG, Lui HM, Lin SL, Lee JM, Ying SY. Regulation of cell proliferation, apoptosis, and carcinogenesis by activin. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2002;227:75–87. - PubMed
-
- Lee YJ, Hong KH, Yun J, Oh SP. Generation of activin receptor type IIB isoform-specific hypomorphic alleles. Genesis. 2006;44:487–494. - PubMed
-
- Mori Y, Yin J, Rashid A, Leggett BA, Young J, et al. Instabilotyping: comprehensive identification of frameshift mutations caused by coding region microsatellite instability. Cancer Res. 2001;61:6046–6049. - PubMed
-
- Hempen PM, Zhang L, Bansal RK, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Murphy KM, et al. Evidence of selection for clones having genetic inactivation of the activin A type II receptor (ACVR2) gene in gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Res. 2003;63:994–999. - PubMed
-
- Deacu E, Mori Y, Sato F, Yin J, Olaru A, et al. Activin type II receptor restoration in ACVR2-deficient colon cancer cells induces transforming growth factor-beta response pathway genes. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7690–7696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

