FoxQ1 overexpression influences poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer, associates with the phenomenon of EMT
- PMID: 22761930
- PMCID: PMC3386178
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039937
FoxQ1 overexpression influences poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer, associates with the phenomenon of EMT
Abstract
Background: We determined the expression of forkhead box Q1 (FoxQ1), E-cadherin (E-cad), Mucin 1 (MUC1), vimentin (VIM) and S100 calcium binding protein A4 (S100A4), all epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) indicator proteins in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tissue samples. We also investigated the relationship between these five proteins expression and other clinicopathologic factors in NSCLC. Finally, we assessed the potential value of these markers as prognostic indicators of survival in NSCLC's patients.
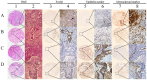
Methods: Quantitative real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry were used to characterize the expression of the FoxQ1 mRNA and protein in NSCLC. Expression of transcripts and translated products for the other four EMT indicator proteins was assessed by immunohistochemistry in the same clinical NSCLC samples.
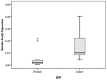
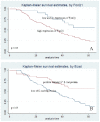
Results: FoxQ1 mRNA and protein were up-regulated in NSCLC compared with normal tissues (P = 0.015 and P<0.001, respectively). Expression of FoxQ1 in adenocarcinoma was higher than in squamous cell carcinoma (P = 0.005), and high expression of FoxQ1 correlated with loss of E-cad expression (P = 0.012), and anomalous positivity of VIM (P = 0.024) and S100A4 (P = 0.004). Additional survival analysis showed that high expression of FoxQ1 (P = 0.047) and E-cad (P = 0.021) were independent prognostic factors.
Conclusion: FoxQ1 maybe plays a specific role in the EMT of NSCLC, and could be used as a prognostic factor for NSCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Cagle PT, Allen TC, Dacic S, Beasley MB, Borczuk AC, et al. Revolution in lung cancer: new challenges for the surgical pathologist. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:110–116. - PubMed
-
- Wen C, Dehnel T. China wrestles with lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:15. - PubMed
-
- Gao W, Liu L, Lu X, Shu Y. Circulating microRNAs: possible prediction biomarkers for personalized therapy of non-small-cell lung carcinoma. Clin Lung Cancer. 2011;12:14–17. - PubMed
-
- Smith CB, Kelley AS, Meier DE. Evidence for new standard of care in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;22:193–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

