DOK3 negatively regulates LPS responses and endotoxin tolerance
- PMID: 22761938
- PMCID: PMC3384629
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039967
DOK3 negatively regulates LPS responses and endotoxin tolerance
Abstract
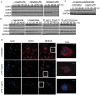
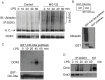
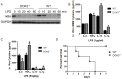
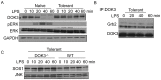
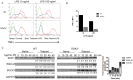
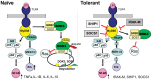
Innate immune activation via Toll-like receptors (TLRs), although critical for host defense against infection, must be regulated to prevent sustained cell activation that can lead to cell death. Cells repeatedly stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) develop endotoxin tolerance making the cells hypo-responsive to additional TLR stimulation. We show here that DOK3 is a negative regulator of TLR signaling by limiting LPS-induced ERK activation and cytokine responses in macrophages. LPS induces ubiquitin-mediated degradation of DOK3 leading to SOS1 degradation and inhibition of ERK activation. DOK3 mice are hypersensitive to sublethal doses of LPS and have altered cytokine responses in vivo. During endotoxin tolerance, DOK3 expression remains stable, and it negatively regulates the expression of SHIP1, IRAK-M, SOCS1, and SOS1. As such, DOK3-deficient macrophages are more sensitive to LPS-induced tolerance becoming tolerant at lower levels of LPS than wild type cells. Taken together, the absence of DOK3 increases LPS signaling, contributing to LPS-induced tolerance. Thus, DOK3 plays a role in TLR signaling during both naïve and endotoxin-induced tolerant conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Janeway CA, Jr, Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Nagai Y, Akashi S, Nagafuku M, Ogata M, Iwakura Y, et al. Essential role of MD-2 in LPS responsiveness and TLR4 distribution. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:667–672. - PubMed
-
- Takeda K, Kaisho T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:335–376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

