IL-18 Serum Level in Adult Onset Still's Disease: A Marker of Disease Activity
- PMID: 22762008
- PMCID: PMC3385601
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/156890
IL-18 Serum Level in Adult Onset Still's Disease: A Marker of Disease Activity
Abstract
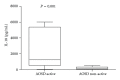
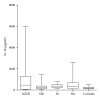
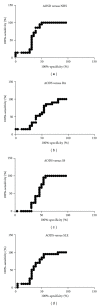
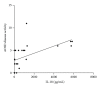
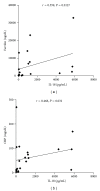
Introduction. Immunological factors seem to play a pivotal role in Adult Onset Still's Disease (AOSD). Among all, IL-18 cytokine is overexpressed and drives the inflammatory process. Objective. We aimed to investigate the levels of IL-18 in sera of Italian patients with AOSD and to assess its possible role as a marker of disease activity. Methods. IL-18 serum levels were determined by ELISA in 26 Italian patients with AOSD. Disease activity was assessed using Pouchot's criteria. As controls, 21 patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), 21 patients with Sjogren's Syndrome (SS), 20 patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), and 21 healthy subjects (normal human sera, NHS) were evaluated. Results. IL-18 serum levels were significantly higher in patients with active AOSD than in non-active (P = 0.001) and control groups (RA P = 0.0070, SS P = 0.0029, SLE P = 0.0032, NHS P = 0.0004). A significant correlation between IL-18 serum levels and disease activity (P < 0.0001), and laboratory parameters as ferritin (P = 0.0127) and C-reactive protein (P = 0.0032) was demonstrated. Conclusions. Higher levels of IL-18 are detected in active AODS patients and correlate with disease activity and inflammatory laboratory features. ROC-AUC analysis of the serum concentration of IL-18 suggests that it can be considered a diagnostic marker of AOSD. This paper supports the targeting of this cytokine as a possible therapeutic option in AOSD.
Figures
References
-
- Ohta A, Yamaguchi M, Kaneoka H, Nagayoshi T, Hiida M. Adult Still’s disease: review of 228 cases from the literature. Journal of Rheumatology. 1988;14(6):1139–1146. - PubMed
-
- Wakai K, Ohta A, Tamakoshi A, et al. Estimated prevalence and incidence of adult Still’s disease: findings by a nationwide epidemiological survey in Japan. Journal of Epidemiology. 1997;7(4):221–225. - PubMed
-
- Ohta A, Yamaguchi M, Tsunematsu T, et al. Adult Still’s disease: a multicenter survey of Japanese patients. Journal of Rheumatology. 1990;17(8):1058–1063. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

