Signal transduction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptors
- PMID: 22762016
- PMCID: PMC3385940
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006502
Signal transduction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptors
Abstract
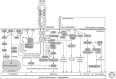
Vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) are master regulators of vascular development and of blood and lymphatic vessel function during health and disease in the adult. It is therefore important to understand the mechanism of action of this family of five mammalian ligands, which act through three receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). In addition, coreceptors like neuropilins (NRPs) and integrins associate with the ligand/receptor signaling complex and modulate the output. Therapeutics to block several of the VEGF signaling components have been developed with the aim to halt blood vessel formation, angiogenesis, in diseases that involve tissue growth and inflammation, such as cancer. In this review, we outline the current information on VEGF signal transduction in relation to blood and lymphatic vessel biology.
Figures
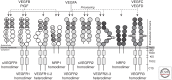


References
-
- Aase K, von Euler G, Li X, Ponten A, Thoren P, Cao R, Cao Y, Olofsson B, Gebre-Medhin S, Pekny M, et al. 2001. Vascular endothelial growth factor-B–deficient mice display an atrial conduction defect. Circulation 104: 358–364 - PubMed
-
- Alam A, Herault JP, Barron P, Favier B, Fons P, Delesque-Touchard N, Senegas I, Laboudie P, Bonnin J, Cassan C, et al. 2004. Heterodimerization with vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) is necessary for VEGFR-3 activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 324: 909–915 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
