Protective effect of saturated hydrogen saline against blue light-induced retinal damage in rats
- PMID: 22762040
- PMCID: PMC3359028
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2012.02.07
Protective effect of saturated hydrogen saline against blue light-induced retinal damage in rats
Abstract
Aim: To explore the effect of saturated hydrogen saline on blue light-induced retinal damage in rats.
Methods: The retinal damage of rats was induced by blue light exposure for 6 hours and examined 8 hours, 16 hours and 24 hours after the exposure. One hundred female Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into four groups. Group 1 included 30 rats received light exposure without any other treatment. Group 2 included 30 rats received light exposure with intraperitoneal injection of normal saline. Group 3 included 30 rats received light exposure with intraperitoneal injection of saturated hydrogen saline. And Group 4 included the other 10 rats which did not receive any treatment. The amount of intraperitoneal injection of saturated hydrogen saline and normal saline was calculated in the ratio of 1ml/100g of rat weight. Specimens were collected and processed by H-E staining, ultrastructure observation, biochemical measurement. Morphological changes were observed by light microscope and transmission electron microscope (TEM) and the retinal outer nuclear layer (ONL) thickness was measured by IPP 6.0, while the malondialdehyde (MDA) was measured by colorimetric determination at 532 nm.
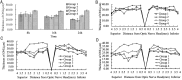
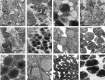
Results: Although the structure of retina in Group 1 and Group 2 was injured heavily, the injury in Group 3 was mild. The differences between Group 1 and Group 2 were not significant. Compared with the rats in Group 1 and Group 2, the ones in Group 3 had more clearly demarcated retina structure and more ordered cells by light microscope and TEM observation. The ONL thicknesses (400 times) of four groups at each time point except between Group 1 and Group 2 were significantly different (P<0.05). The thicknesses of the ONL in Group 1 at three time points were 30.41±4.04µm, 26.11±2.82µm and 20.63±1.06µm, in Group 2 were 31.62±4.54µm, 25.08±3.63µm and 19.07±3.86µm, in Group 3 were 29.75±3.62µm, 28.83±1.97µm and 27.61±1.83µm. In Group 4 the mean of the thickness was 37.35±1.37µm. As time went by, the damage grew more severely. At 24h point, the differences were most significant. Compared with Group 4, the thickness was 46.23% thinner in Group 1, 50.29% thinner in Group 2 and 28.04% thinner in Group 3. The stack structures of membranous disc in Group 3 were injured slightly, but in Group 1 and Group 2 the damage was more obvious by TEM. Compared with Group 4 at each time point, the content of MDA in Group 1 was higher (P<0.05). The content of MDA in Group 3 was significantly lower than those of Group 1 (P<0.05) and Group 2 (P<0.05). Between the Group 1 and Group 2, the MDA concentration at each time point was no significant difference (P>0.05).
Conclusion: Saturated hydrogen saline could protect the retina from light-induced damage by attenuating oxidative stress.
Keywords: antioxidants; hydrogen; phototoxicity; retina.
Figures

References
-
- Beatty S, Koh H, Phil M, Henson D, Boulton M. The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. Surv Ophthalmol. 2000;45:115–134. - PubMed
-
- Drobek-Slowik M, Karczewicz D, Safranow K. The potential role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of the age-related macular degeneration (AMD) Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online) 2007;61:28–37. - PubMed
-
- Rozanowska M, Jarvis-Evans J, Korytowski W, Boulton ME, Burke JM, Sarna T. Blue light-induced reactivity of retinal age pigment. In vitro generation of oxygen-reactive species. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:18825–18830. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
