Identification of new susceptibility loci for osteoarthritis (arcOGEN): a genome-wide association study
- PMID: 22763110
- PMCID: PMC3443899
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60681-3
Identification of new susceptibility loci for osteoarthritis (arcOGEN): a genome-wide association study
Abstract
Background: Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis worldwide and is a major cause of pain and disability in elderly people. The health economic burden of osteoarthritis is increasing commensurate with obesity prevalence and longevity. Osteoarthritis has a strong genetic component but the success of previous genetic studies has been restricted due to insufficient sample sizes and phenotype heterogeneity.
Methods: We undertook a large genome-wide association study (GWAS) in 7410 unrelated and retrospectively and prospectively selected patients with severe osteoarthritis in the arcOGEN study, 80% of whom had undergone total joint replacement, and 11,009 unrelated controls from the UK. We replicated the most promising signals in an independent set of up to 7473 cases and 42,938 controls, from studies in Iceland, Estonia, the Netherlands, and the UK. All patients and controls were of European descent.
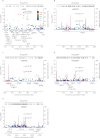
Findings: We identified five genome-wide significant loci (binomial test p≤5·0×10(-8)) for association with osteoarthritis and three loci just below this threshold. The strongest association was on chromosome 3 with rs6976 (odds ratio 1·12 [95% CI 1·08-1·16]; p=7·24×10(-11)), which is in perfect linkage disequilibrium with rs11177. This SNP encodes a missense polymorphism within the nucleostemin-encoding gene GNL3. Levels of nucleostemin were raised in chondrocytes from patients with osteoarthritis in functional studies. Other significant loci were on chromosome 9 close to ASTN2, chromosome 6 between FILIP1 and SENP6, chromosome 12 close to KLHDC5 and PTHLH, and in another region of chromosome 12 close to CHST11. One of the signals close to genome-wide significance was within the FTO gene, which is involved in regulation of bodyweight-a strong risk factor for osteoarthritis. All risk variants were common in frequency and exerted small effects.
Interpretation: Our findings provide insight into the genetics of arthritis and identify new pathways that might be amenable to future therapeutic intervention.
Funding: arcOGEN was funded by a special purpose grant from Arthritis Research UK.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Osteoarthritis susceptibility genes continue trickling in.Lancet. 2012 Sep 1;380(9844):785-7. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60818-6. Epub 2012 Jul 3. Lancet. 2012. PMID: 22763109 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Genome-wide association study for osteoarthritis.Lancet. 2013 Feb 2;381(9864):372-3; discussion 373. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60167-1. Lancet. 2013. PMID: 23374473 No abstract available.
References
-
- Dieppe PA, Lohmander LS. Pathogenesis and management of pain in osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2005;365:965–973. - PubMed
-
- Valdes AM, Spector TD. Genetic epidemiology of hip and knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7:23–32. - PubMed
-
- Loughlin J. The genetic epidemiology of human primary osteoarthritis: current status. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2005;7:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Valdes AM, McWilliams D, Arden NK. Involvement of different risk factors in clinically severe large joint osteoarthritis according to the presence of hand interphalangeal nodes. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2688–2695. - PubMed
-
- Chapman K, Takahashi A, Meulenbelt I. A meta-analysis of European and Asian cohorts reveals a global role of a functional SNP in the 5′ UTR of GDF5 with osteoarthritis susceptibility. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:1497–1504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

