Estradiol selectively reduces central neural activation induced by hypertonic NaCl infusion in ovariectomized rats
- PMID: 22763321
- PMCID: PMC3590917
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2012.06.015
Estradiol selectively reduces central neural activation induced by hypertonic NaCl infusion in ovariectomized rats
Abstract
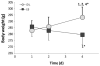
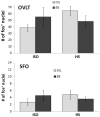
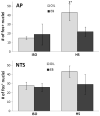
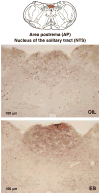
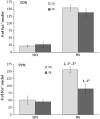
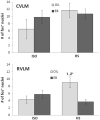
We recently reported that the latency to begin drinking water during slow, intravenous infusion of a concentrated NaCl solution was shorter in estradiol-treated ovariectomized rats compared to oil vehicle-treated rats, despite comparably elevated plasma osmolality. To test the hypothesis that the decreased latency to begin drinking is attributable to enhanced detection of increased plasma osmolality by osmoreceptors located in the CNS, the present study used immunocytochemical methods to label fos, a marker of neural activation. Increased plasma osmolality did not activate the subfornical organ (SFO), organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis (OVLT), or the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) in either oil vehicle-treated rats or estradiol-treated rats. In contrast, hyperosmolality increased fos labeling in the area postrema (AP), the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN) and the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) in both groups; however, the increase was blunted in estradiol-treated rats. These results suggest that estradiol has selective effects on the sensitivity of a population of osmo-/Na(+)-receptors located in the AP, which, in turn, alters activity in other central areas associated with responses to increased osmolality. In conjunction with previous reports that hyperosmolality increases blood pressure and that elevated blood pressure inhibits drinking, the current findings of reduced activation in AP, PVN, and RVLM-areas involved in sympathetic nerve activity-raise the possibility that estradiol blunts HS-induced blood pressure changes. Thus, estradiol may eliminate or reduce the initial inhibition of water intake that occurs during increased osmolality, and facilitate a more rapid behavioral response, as we observed in our recent study.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Andersen LJ, Jensen TU, Bestle MH, Bie P. Gastrointestinal osmoreceptors and renal sodium excretion in humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2000;278:R287–94. - PubMed
-
- Barron WM, Schreiber J, Lindheimer MD. Effect of ovarian sex steroids on osmoregulation and vasopressin secretion in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1986;250:E352–61. - PubMed
-
- Bealer SL. Central control of cardiac baroreflex responses during peripheral hyperosmolality. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2000;278:R1157–63. - PubMed
-
- Bisley JW, Rees SM, McKinley MJ, Hards DK, Oldfield BJ. Identification of osmoresponsive neurons in the forebrain of the rat: a Fos study at the ultrastructural level. Brain Res. 1996;720:25–34. - PubMed
-
- Bossmar T, Forsling M, Akerlund M. Circulating oxytocin and vasopressin is influenced by ovarian steroid replacement in women. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1995;74:544–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

