Carnosine prevents necrotic and apoptotic death of rat thymocytes via ouabain-sensitive Na/K-ATPase
- PMID: 22763713
- PMCID: PMC3481008
- DOI: 10.1002/cbf.2856
Carnosine prevents necrotic and apoptotic death of rat thymocytes via ouabain-sensitive Na/K-ATPase
Abstract
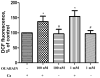
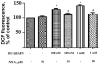
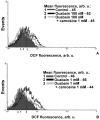
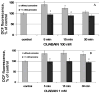
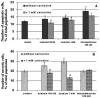
It is known that ouabain, a selective inhibitor of Na/K-ATPase, not only can cause the activation of signal cascades, which regulate the cell viability, but also can cause the accumulation of free radicals, which can evoke the oxidative stress. We have shown that the nanomolar concentrations of ouabain result in the temporary increase in the level of intracellular free radicals, but the millimolar concentration of ouabain induces a stable intracellular accumulation of free radicals in rat thymocytes. The increasing level of free radicals resulting from both low and high concentrations of ouabain can be attenuated by the antioxidant, carnosine. Moreover, the long-term incubation with ouabain leads to the cell death by necrosis and apoptosis. Ouabain-mediated apoptosis and necrosis were also abolished by carnosine.
Copyright © 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
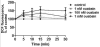
Similar articles
-
Low doses of ouabain protect from serum deprivation-triggered apoptosis and stimulate kidney cell proliferation via activation of NF-kappaB.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006 Jul;17(7):1848-57. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005080894. Epub 2006 May 17. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006. PMID: 16707566
-
Ionic mechanism of ouabain-induced concurrent apoptosis and necrosis in individual cultured cortical neurons.J Neurosci. 2002 Feb 15;22(4):1350-62. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-04-01350.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11850462 Free PMC article.
-
Low-dose ouabain protects against excitotoxic apoptosis and up-regulates nuclear Bcl-2 in vivo.Neuroscience. 2006;137(1):133-44. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.10.004. Epub 2005 Nov 16. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16297565
-
Molecular mechanisms of Na/K-ATPase-mediated signal transduction.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 Apr;986:497-503. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07234.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 12763870 Review.
-
Ouabain antagonists as antihypertensive agents.Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(25):3301-5. doi: 10.2174/138161205774424735. Curr Pharm Des. 2005. PMID: 16250857 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroinflammation and Neutrophils: Modulation by Ouabain.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 31;13:824907. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.824907. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35173621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Much More than a Cardiotonic Steroid: Modulation of Inflammation by Ouabain.Front Physiol. 2017 Nov 10;8:895. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00895. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 29176951 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Skou J, Esmann M. The Na,K-ATPase. Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992;24(3):249–261. - PubMed
-
- Kometiani P, Li J, Gnudi L, Kahn BB, Askari A, Xie Z. Multiple signal transduction pathways link Na/K-ATPase to growth-related genes in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:15249–15256. - PubMed
-
- Bulygina ER, Lyapina LY, Boldyrev AA. Activation of glutamate receptors inhibits Na/K-ATPase of cerebellum granule cells. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2002;67(9):1001–1005. - PubMed
-
- Karitskaya I, Aksenov N, Vassilieva I, Zenin V, Marakhova I. Long-term regulation of Na,K-ATPase pump during T-cell proliferation. Pflugers Arch. 2010;460(4):777–789. - PubMed
-
- Karpova L, Eva A, Kirch U, Boldyrev A, Scheiner-Bobis G. Sodium pump alpha1 and alpha3 subunit isoforms mediate distinct responses to ouabain and are both essential for survival of human neuroblastoma. FEBS J. 2010;277(8):1853–1860. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

