Sulfation of ractopamine and salbutamol by the human cytosolic sulfotransferases
- PMID: 22763752
- PMCID: PMC3529569
- DOI: 10.1093/jb/mvs073
Sulfation of ractopamine and salbutamol by the human cytosolic sulfotransferases
Abstract
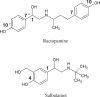
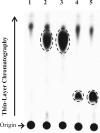
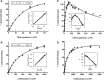
Feed additives such as ractopamine and salbutamol are pharmacologically active compounds, acting primarily as β-adrenergic agonists. This study was designed to investigate whether the sulfation of ractopamine and salbutamol may occur under the metabolic conditions and to identify the human cytosolic sulfotransferases (SULTs) that are capable of sulfating two major feed additive compounds, ractopamine and salbutamol. A metabolic labelling study showed the generation and release of [(35)S]sulfated ractopamine and salbutamol by HepG2 human hepatoma cells labelled with [(35)S]sulfate in the presence of these two compounds. A systematic analysis using 11 purified human SULTs revealed SULT1A3 as the major SULT responsible for the sulfation of ractopamine and salbutamol. The pH dependence and kinetic parameters were analyzed. Moreover, the inhibitory effects of ractopamine and salbutamol on SULT1A3-mediated dopamine sulfation were investigated. Cytosol or S9 fractions of human lung, liver, kidney and small intestine were examined to verify the presence of ractopamine-/salbutamol-sulfating activity in vivo. Of the four human organs, the small intestine displayed the highest activity towards both compounds. Collectively, these results imply that the sulfation mediated by SULT1A3 may play an important role in the metabolism and detoxification of ractopamine and salbutamol.
Figures



References
-
- Sillence MN. Technologies for the control of fat and lean deposition in livestock. Vet. J. 2004;167:242–257. - PubMed
-
- Strydom PE, Frylinck L, Montgomery JL, Smith MF. The comparison of three beta-agonists for growth performance, carcass, characteristics and meat quality of feedlot cattle. Meat. Sci. 2009;81:557–564. - PubMed
-
- Mimbs KJ, Pringle TD, Azain MJ, Meers SA, Armstrong TA. Effects of ractopamine on performance and composition of pigs phenotypically sorted into fat and lean groups. J. Anim. Sci. 2005;83:1361–1369. - PubMed
-
- Baker PK, Dalrymple RH, Ingle DL, Ricks CA. Use of a beta-adrenergic agonist to alter muscle and fat deposition in lambs. J. Anim. Sci. 1984;59:1256–1261.
-
- Hansen JA, Nelssen JL, Goodband RD, Laurin JL. Interactive effects among porcine somatotropin, the beta-adrenergic agonist salbutamol, and dietary lysine on growth performance and nitrogen balance of finishing swine. J. Anim. Sci. 1994;72:1540–1547. - PubMed

