Expression of mRNAs for PPT, CGRP, NF-200, and MAP-2 in cocultures of dissociated DRG neurons and skeletal muscle cells in administration of NGF or NT-3
- PMID: 22763971
- PMCID: PMC3703251
- DOI: 10.5603/fhc.2012.0041
Expression of mRNAs for PPT, CGRP, NF-200, and MAP-2 in cocultures of dissociated DRG neurons and skeletal muscle cells in administration of NGF or NT-3
Abstract
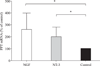
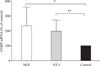
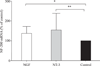
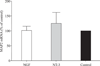
Both neurotrophins (NTs) and target skeletal muscle (SKM) cells are essential for the maintenance of the function of neurons and nerve-muscle communication. However, much less is known about the association of target SKM cells with distinct NTs on the expression of mRNAs for preprotachykinin (PPT), calcitonin-gene related peptide (CGRP), neurofilament 200 (NF-200), and microtubule associated protein 2 (MAP-2) in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) sensory neurons. In the present study, a neuromuscular coculture model of dissociated dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons and SKM cells was established. The morphology of DRG neurons and SKM cells in coculture was observed with an inverted phase contrast microscope. The effects of nerve growth factor (NGF) or neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) on the expression of mRNAs for PPT, CGRP, NF-200, and MAP-2 was analyzed by real time-PCR assay. The morphology of DRG neuronal cell bodies and SKM cells in neuromuscular coculture at different conditions was similar. The neurons presented evidence of dense neurite outgrowth in the presence of distinct NTs in neuromuscular cocultures. NGF and NT-3 increased mRNA levels of PPT, CGRP, and NF-200, but not MAP-2, in neuromuscular cocultures. These results offer new clues towards a better understanding of the association of target SKM cells with distinct NTs on the expression of mRNAs for PPT, CGRP, NF-200 and MAP-2, and implicate the association of target SKM cells and NTs with DRG sensory neuronal phenotypes.
Figures

References
-
- Howe CL, Valletta JS, Rusnak AS, et al. NGF signaling from clathrin-coated vesicles: Evidence that signaling endosomes serve as a platform for the Ras-MAPK pathway. Neuron. 2001;32:801–814. - PubMed
-
- Zhao C, Veltri K, Li S, et al. NGF, BDNF, NT-3, and GDNF mRNA expression in rat skeletal muscle following denervation and sensory protection. J Neurotrauma. 2004;21:1468–1478. - PubMed
-
- Lu J, Zhou XF, Rush RA. Small primary sensory neurons innervating epidermis and viscera display differential phenotype in the adult rat. Neurosci Res. 2001;41:355–363. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Liu Z, Liu H, et al. Neuronal phenotype and tyrosine kinase receptor expression in cocultures of dorsal root ganglion and skeletal muscle cells. Anat Rec. 2009;292:107–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

