Pharmacological rescue of mitochondrial deficits in iPSC-derived neural cells from patients with familial Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 22764206
- PMCID: PMC3462009
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003985
Pharmacological rescue of mitochondrial deficits in iPSC-derived neural cells from patients with familial Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder caused by genetic and environmental factors that results in degeneration of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway in the brain. We analyzed neural cells generated from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) derived from PD patients and presymptomatic individuals carrying mutations in the PINK1 (PTEN-induced putative kinase 1) and LRRK2 (leucine-rich repeat kinase 2) genes, and compared them to those of healthy control subjects. We measured several aspects of mitochondrial responses in the iPSC-derived neural cells including production of reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial respiration, proton leakage, and intraneuronal movement of mitochondria. Cellular vulnerability associated with mitochondrial dysfunction in iPSC-derived neural cells from familial PD patients and at-risk individuals could be rescued with coenzyme Q(10), rapamycin, or the LRRK2 kinase inhibitor GW5074. Analysis of mitochondrial responses in iPSC-derived neural cells from PD patients carrying different mutations provides insight into convergence of cellular disease mechanisms between different familial forms of PD and highlights the importance of oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in this neurodegenerative disease.
Figures



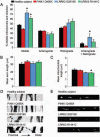
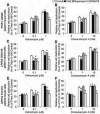

References
-
- Langston JW, Ballard P, Tetrud JW, Irwin I. Chronic parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine analog synthesis. Science. 1983;219:979. - PubMed
-
- Gorell JM, Johnson CC, Rybicki BA, Peterson EL, Richardson RJ. The risk of Parkinson's disease with exposure to pesticides, farming, well water, and rural living. Neurology. 1998;50(5):1346–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS38377/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000064/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- NS057567/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS072187/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 NS070276/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1U24NS078338-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS038377/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS036630/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 NS078338/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS036630/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1RC2NS070276/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057567/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS061856/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50NS072187/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

