Regulation of arrestin translocation by Ca2+ and myosin III in Drosophila photoreceptors
- PMID: 22764229
- PMCID: PMC6622236
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0924-12.2012
Regulation of arrestin translocation by Ca2+ and myosin III in Drosophila photoreceptors
Abstract
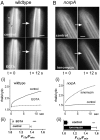
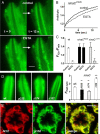
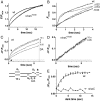
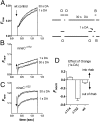
Upon illumination several phototransduction proteins translocate between cell body and photosensory compartments. In Drosophila photoreceptors arrestin (Arr2) translocates from cell body to the microvillar rhabdomere down a diffusion gradient created by binding of Arr2 to photo-isomerized metarhodopsin. Translocation is profoundly slowed in mutants of key phototransduction proteins including phospholipase C (PLC) and the Ca(2+)-permeable transient receptor potential channel (TRP), but how the phototransduction cascade accelerates Arr2 translocation is unknown. Using real-time fluorescent imaging of Arr2-green fluorescent protein translocation in dissociated ommatidia, we show that translocation is profoundly slowed in Ca(2+)-free solutions. Conversely, in a blind PLC mutant with ∼100-fold slower translocation, rapid translocation was rescued by the Ca(2+) ionophore, ionomycin. In mutants lacking NINAC (calmodulin [CaM] binding myosin III) in the cell body, translocation remained rapid even in Ca(2+)-free solutions. Immunolabeling revealed that Arr2 in the cell body colocalized with NINAC in the dark. In intact eyes, the impaired translocation found in trp mutants was rescued in ninaC;trp double mutants. Nevertheless, translocation following prolonged dark adaptation was significantly slower in ninaC mutants, than in wild type: a difference that was reflected in the slow decay of the electroretinogram. The results suggest that cytosolic NINAC is a Ca(2+)-dependent binding target for Arr2, which protects Arr2 from immobilization by a second potential sink that sequesters and releases arrestin on a much slower timescale. We propose that rapid Ca(2+)/CaM-dependent release of Arr2 from NINAC upon Ca(2+) influx accounts for the acceleration of translocation by phototransduction.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Light-dependent translocation of visual arrestin regulated by the NINAC myosin III.Neuron. 2004 Jul 8;43(1):95-103. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.06.014. Neuron. 2004. PMID: 15233920
-
Arrestin translocation is stoichiometric to rhodopsin isomerization and accelerated by phototransduction in Drosophila photoreceptors.Neuron. 2010 Sep 23;67(6):997-1008. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.08.024. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 20869596 Free PMC article.
-
Subcellular translocation of the eGFP-tagged TRPL channel in Drosophila photoreceptors requires activation of the phototransduction cascade.J Cell Sci. 2006 Jun 15;119(Pt 12):2592-603. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02986. Epub 2006 May 30. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 16735439 Free PMC article.
-
Light-regulated translocation of signaling proteins in Drosophila photoreceptors.J Physiol Paris. 2006 Mar-May;99(2-3):133-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jphysparis.2005.12.010. Epub 2006 Feb 3. J Physiol Paris. 2006. PMID: 16458490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ectoplasm, ghost in the R cell machine?Dev Neurobiol. 2011 Dec;71(12):1246-57. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20898. Dev Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21542135 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Depletion of PtdIns(4,5)P₂ underlies retinal degeneration in Drosophila trp mutants.J Cell Sci. 2013 Mar 1;126(Pt 5):1247-59. doi: 10.1242/jcs.120592. Epub 2013 Feb 1. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23378018 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo identification of Drosophila rhodopsin interaction partners by biotin proximity labeling.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 23;14(1):1986. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52041-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38263196 Free PMC article.
-
Differential activation of rhodopsin triggers distinct endocytic trafficking and recycling in vivo via differential phosphorylation.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 7;19(6):e0303882. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303882. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38848405 Free PMC article.
-
Elementary and macroscopic light-induced currents and their Ca(2+)-dependence in the photoreceptors of Periplaneta americana.Front Physiol. 2014 Apr 22;5:153. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00153. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24795648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alloway PG, Howard L, Dolph PJ. The formation of stable rhodopsin-arrestin complexes induces apoptosis and photoreceptor cell degeneration. Neuron. 2000;28:129–138. - PubMed
-
- Bloomquist BT, Shortridge RD, Schneuwly S, Perdew M, Montell C, Steller H, Rubin G, Pak WL. Isolation of putative phospholipase C gene of Drosophila, norpA and its role in phototransduction. Cell. 1988;54:723–733. - PubMed
-
- Broekhuyse RM, Tolhuizen EF, Janssen AP, Winkens HJ. Light induced shift and binding of S-antigen in retinal rods. Curr Eye Res. 1985;4:613–618. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
