Plant natural compounds: targeting pathways of autophagy as anti-cancer therapeutic agents
- PMID: 22765290
- PMCID: PMC6496896
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2012.00833.x
Plant natural compounds: targeting pathways of autophagy as anti-cancer therapeutic agents
Abstract
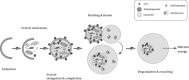
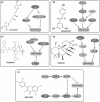
Natural compounds derived from plant sources are well characterized as possessing a wide variety of remarkable anti-tumour properties, for example modulating programmed cell death, primarily referring to apoptosis, and autophagy. Distinct from apoptosis, autophagy (an evolutionarily conserved, multi-step lysosomal degradation process in which a cell destroys long-lived proteins and damaged organelles) may play crucial regulatory roles in many pathological processes, most notably in cancer. In this review, we focus on highlighting several representative plant natural compounds such as curcumin, resveratrol, paclitaxel, oridonin, quercetin and plant lectin - that may lead to cancer cell death - for regulation of some core autophagic pathways, involved in Ras-Raf signalling, Beclin-1 interactome, BCR-ABL, PI3KCI/Akt/mTOR, FOXO1 signalling and p53. Taken together, these findings would provide a new perspective for exploiting more plant natural compounds as potential novel anti-tumour drugs, by targeting the pathways of autophagy, for future cancer therapeutics.
© 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 61, 69–90. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144, 646–674. - PubMed
-
- Liu JJ, Lin M, Yu JY, Liu B, Bao JK (2011) Targeting apoptotic and autophagic pathways for cancer therapeutics. Cancer Lett. 300, 105–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

