Five-group cytogenetic risk classification, monosomal karyotype, and outcome after hematopoietic cell transplantation for MDS or acute leukemia evolving from MDS
- PMID: 22767498
- PMCID: PMC3478516
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-04-423046
Five-group cytogenetic risk classification, monosomal karyotype, and outcome after hematopoietic cell transplantation for MDS or acute leukemia evolving from MDS
Abstract
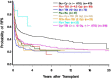
Clonal cytogenetic abnormalities are a major risk factor for relapse after hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) for myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). We determined the impact of the recently established 5-group cytogenetic classification of MDS on outcome after HCT. Results were compared with the impact of the International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) 3 cytogenetic risk groups, and the additional effect of a monosomal karyotype was assessed. The study included data on 1007 patients, 1-75 years old (median 45 years), transplanted from related (n = 547) or unrelated (n = 460) donors. Various conditioning regimens were used, and marrow, peripheral blood, or cord blood served as stem cell source. Both IPSS and 5-group cytogenetic risk classifications were significantly associated with post-HCT relapse and mortality, but the 5-group classification discriminated more clearly among the lowest- and highest-risk patients. A monosomal karyotype tended to further increase the rates of relapse and mortality, even after considering the IPSS or 5-group classifications. In addition, the pathologic disease category correlated with both relapse and mortality. Mortality was also impacted by patient age, donor type, conditioning regimen, platelet count, and etiology of MDS. Although mortality declined significantly in recent years, novel strategies are needed to overcome the barrier of high-risk cytogenetics.
Figures



References
-
- Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes [erratum appears in Blood. 1998;91(3):1100]. Blood. 1997;89(6):2079–2088. - PubMed
-
- Malcovati L, Germing U, Kuendgen A, et al. A WHO classification-based prognostic scoring system (WPSS) for predicting survival in myelodysplastic syndromes [abstract]. Blood. 2005;106(11):232a–233a. Abstract 788.
-
- Malcovati L, Germing U, Kuendgen A, et al. Time-dependent prognostic scoring system for predicting survival and leukemic evolution in myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(23):3503–3510. - PubMed
-
- Alessandrino EP, Della Porta MG, Bacigalupo A, et al. WHO classification and WPSS predict posttransplantation outcome in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome: a study from the Gruppo Italiano Trapianto di Midollo Osseo (GITMO). Blood. 2008;112(3):895–902. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- CA078902/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL095999/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL088021/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA018029/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA138720/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL062946/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL036444/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095999/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA078902/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL036444/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA018029/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

