Bacterial sepsis and GI tract GVHD: more commensal than you think
- PMID: 22767576
- PMCID: PMC6413962
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-05-427435
Bacterial sepsis and GI tract GVHD: more commensal than you think
Abstract
Even in 2012, almost 45 years after the first successful allogeneic bone marrow transplants, infection remains the most common cause of nonrelapse transplant-related mortality.(1)
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The author declares no competing financial interests. ■
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The author declares no competing financial interests. ■
Figures
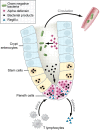
Comment on
-
Graft-versus-host disease disrupts intestinal microbial ecology by inhibiting Paneth cell production of α-defensins.Blood. 2012 Jul 5;120(1):223-31. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-401166. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22535662
References
-
- Chakraverty R, Peggs K, Chopra R, et al. Limiting transplantation-related mortality following unrelated donor stem cell transplantation by using a nonmyeloablative conditioning regimen. Blood. 2002;99(3):1071–1078. - PubMed
-
- Serody JS, Shea TC. Prevention of infections in bone marrow transplant recipients. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1997;11(2):459–477. - PubMed
-
- Eriguchi Y, Takashima S, Oka H, et al. Graft-versus-host disease disrupts intestinal microbial ecology by inhibiting Paneth cell production of alpha-defensins. Blood. 2012;120(1):223–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

