Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) activity bound to insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor, which is continuously sustained by IGF-I stimulation, is required for IGF-I-induced cell proliferation
- PMID: 22767591
- PMCID: PMC3436179
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.393074
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) activity bound to insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor, which is continuously sustained by IGF-I stimulation, is required for IGF-I-induced cell proliferation
Abstract
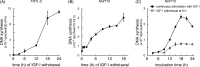
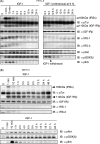
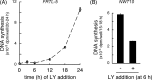
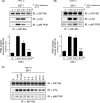
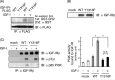
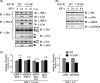
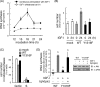
Continuous stimulation of cells with insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) in G(1) phase is a well established requirement for IGF-induced cell proliferation; however, the molecular components of this prolonged signaling pathway that is essential for cell cycle progression from G(1) to S phase are unclear. IGF-I activates IGF-I receptor (IGF-IR) tyrosine kinase, followed by phosphorylation of substrates such as insulin receptor substrates (IRS) leading to binding of signaling molecules containing SH2 domains, including phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) to IRS and activation of the downstream signaling pathways. In this study, we found prolonged (>9 h) association of PI3K with IGF-IR induced by IGF-I stimulation. PI3K activity was present in this complex in thyrocytes and fibroblasts, although tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS was not yet evident after 9 h of IGF-I stimulation. IGF-I withdrawal in mid-G(1) phase impaired the association of PI3K with IGF-IR and suppressed DNA synthesis the same as when PI3K inhibitor was added. Furthermore, we demonstrated that Tyr(1316)-X-X-Met of IGF-IR functioned as a PI3K binding sequence when this tyrosine is phosphorylated. We then analyzed IGF signaling and proliferation of IGF-IR(-/-) fibroblasts expressing exogenous mutant IGF-IR in which Tyr(1316) was substituted with Phe (Y1316F). In these cells, IGF-I stimulation induced tyrosine phosphorylation of IGF-IR and IRS-1/2, but mutated IGF-IR failed to bind PI3K and to induce maximal phosphorylation of GSK3β and cell proliferation in response to IGF-I. Based on these results, we concluded that PI3K activity bound to IGF-IR, which is continuously sustained by IGF-I stimulation, is required for IGF-I-induced cell proliferation.
Figures
References
-
- Jones J. I., Clemmons D. R. (1995) Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr. Rev. 16, 3–34 - PubMed
-
- Jones S. M., Kazlauskas A. (2001) Growth-factor-dependent mitogenesis requires two distinct phases of signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 165–172 - PubMed
-
- Chitnis M. M., Yuen J. S., Protheroe A. S., Pollak M., Macaulay V. M. (2008) The type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 6364–6370 - PubMed
-
- Leof E. B., Wharton W., van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. (1982) Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and somatomedin C regulate G1 progression in competent BALB/c-3T3 cells. Exp. Cell Res. 141, 107–115 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

