Visfatin/pre-B-cell colony-enhancing factor (PBEF), a proinflammatory and cell motility-changing factor in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 22767598
- PMCID: PMC3436531
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.312884
Visfatin/pre-B-cell colony-enhancing factor (PBEF), a proinflammatory and cell motility-changing factor in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
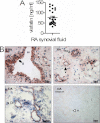
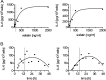
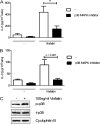
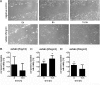
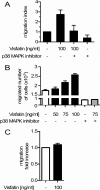
Adipokines such as adiponectin and visfatin/pre-B-cell colony-enhancing factor (PBEF) have been recently shown to contribute to synovial inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In this study, we evaluated the pathophysiological implication of visfatin/PBEF in the molecular patterns of RA synovial tissue, focusing on RA synovial fibroblasts (RASFs), key players in RA synovium. Expression of visfatin/PBEF in synovial fluid and tissue of RA patients was detected by immunoassays and immunohistochemistry. RASFs were stimulated with different concentrations of visfatin/PBEF over varying time intervals, and changes in gene expression were evaluated at the RNA and protein levels using Affymetrix array, real-time PCR, and immunoassays. The signaling pathways involved were identified. The influence of visfatin/PBEF on fibroblast motility and migration was analyzed. In RA synovium, visfatin/PBEF was predominantly expressed in the lining layer, lymphoid aggregates, and interstitial vessels. In RASFs, visfatin/PBEF induced high amounts of chemokines such as IL-8 and MCP-1, proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, and matrix metalloproteinases such as MMP-3. Phosphorylation of p38 MAPK was observed after visfatin/PBEF stimulation, and inhibition of p38 MAPK showed strong reduction of visfatin-induced effects. Directed as well as general fibroblast motility was increased by visfatin/PBEF-induced factors. The results of this study indicate that visfatin/PBEF is involved in synovial fibroblast activation by triggering fibroblast motility and promoting cytokine synthesis at central sites in RA synovium.
Figures
References
-
- Huber L. C., Distler O., Tarner I., Gay R. E., Gay S., Pap T. (2006) Synovial fibroblasts: key players in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 45, 669–675 - PubMed
-
- Lefèvre S., Knedla A., Tennie C., Kampmann A., Wunrau C., Dinser R., Korb A., Schnäker E. M., Tarner I. H., Robbins P. D., Evans C. H., Stürz H., Steinmeyer J., Gay S., Schölmerich J., Pap T., Müller-Ladner U., Neumann E. (2009) Synovial fibroblasts spread rheumatoid arthritis to unaffected joints. Nat. Med. 15, 1414–1420 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kershaw E. E., Flier J. S. (2004) Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 2548–2556 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

