Specific targeting of the metallophosphoesterase YkuE to the bacillus cell wall requires the twin-arginine translocation system
- PMID: 22767609
- PMCID: PMC3436186
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.378190
Specific targeting of the metallophosphoesterase YkuE to the bacillus cell wall requires the twin-arginine translocation system
Abstract
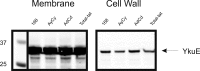
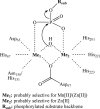
The twin-arginine translocation (Tat) pathway is dedicated to the transport of fully folded proteins across the cytoplasmic membranes of many bacteria and the chloroplast thylakoidal membrane. Accordingly, Tat-dependently translocated proteins are known to be delivered to the periplasm of Gram-negative bacteria, the growth medium of Gram-positive bacteria, and the thylakoid lumen. Here, we present the first example of a protein, YkuE of Bacillus subtilis, that is specifically targeted by the Tat pathway to the cell wall of a Gram-positive bacterium. The cell wall binding of YkuE is facilitated by electrostatic interactions. Interestingly, under particular conditions, YkuE can also be targeted to the cell wall in a Tat-independent manner. The biological function of YkuE was so far unknown. Our present studies show that YkuE is a metal-dependent phosphoesterase that preferentially binds manganese and zinc.
Figures





References
-
- Robinson C., Matos C. F., Beck D., Ren C., Lawrence J., Vasisht N., Mendel S. (2011) Transport and proofreading of proteins by the twin-arginine translocation (Tat) system in bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1808, 876–884 - PubMed
-
- Robinson C, Bolhuis A. (2004) Tat-dependent protein targeting in prokaryotes and chloroplasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1694, 135–147 - PubMed
-
- Tjalsma H., Antelmann H., Jongbloed J. D., Braun P. G., Darmon E., Dorenbos R., Dubois J. Y., Westers H., Zanen G., Quax W. J., Kuipers O. P., Bron S., Hecker M., van Dijl J. M. (2004) Proteomics of protein secretion by Bacillus subtilis. Separating the “secrets” of the secretome. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 68, 207–233 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Palmer T., Sargent F., Berks B. C. (2005) Export of complex cofactor-containing proteins by the bacterial Tat pathway. Trends Microbiol. 13, 175–180 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

