F-spondin/spon1b expression patterns in developing and adult zebrafish
- PMID: 22768035
- PMCID: PMC3387172
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037593
F-spondin/spon1b expression patterns in developing and adult zebrafish
Abstract
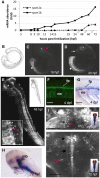
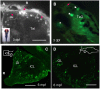
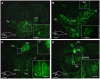
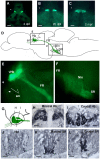
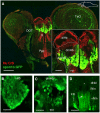
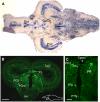
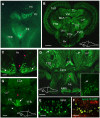
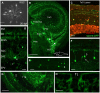
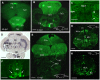
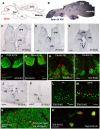
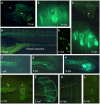
F-spondin, an extracellular matrix protein, is an important player in embryonic morphogenesis and CNS development, but its presence and role later in life remains largely unknown. We generated a transgenic zebrafish in which GFP is expressed under the control of the F-spondin (spon1b) promoter, and used it in combination with complementary techniques to undertake a detailed characterization of the expression patterns of F-spondin in developing and adult brain and periphery. We found that F-spondin is often associated with structures forming long neuronal tracts, including retinal ganglion cells, the olfactory bulb, the habenula, and the nucleus of the medial longitudinal fasciculus (nMLF). F-spondin expression coincides with zones of adult neurogenesis and is abundant in CSF-contacting secretory neurons, especially those in the hypothalamus. Use of this new transgenic model also revealed F-spondin expression patterns in the peripheral CNS, notably in enteric neurons, and in peripheral tissues involved in active patterning or proliferation in adults, including the endoskeleton of zebrafish fins and the continuously regenerating pharyngeal teeth. Moreover, patterning of the regenerating caudal fin following fin amputation in adult zebrafish was associated with F-spondin expression in the blastema, a proliferative region critical for tissue reconstitution. Together, these findings suggest major roles for F-spondin in the CNS and periphery of the developing and adult vertebrate.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bénard C, Hobert O. Looking beyond development: maintaining nervous system architecture. Current topics in developmental biology 87: 175–194. 2009. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19427520. Accessed 16 August 2011. - PubMed
-
- Feinstein Y, Klar A. The neuronal class 2 TSR proteins F-spondin and Mindin: a small family with divergent biological activities. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology 36: 975–980. 2004. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15094111. Accessed 7 February 2010. - PubMed
-
- Woo W-M, Berry EC, Hudson ML, Swale RE, Goncharov A, et al. The C. elegans F-spondin family protein SPON-1 maintains cell adhesion in neural and non-neural tissues. Development (Cambridge, England) 135: 2747–2756. 2008. Available: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=2633776&tool=p.... Accessed 6 November 2011. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klar A, Baldassare M, Jessell TM. F-spondin: a gene expressed at high levels in the floor plate encodes a secreted protein that promotes neural cell adhesion and neurite extension. Cell 69: 95–110. 1992. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1555244. Accessed 7 February 2010. - PubMed
-
- Schubert D, Klar A, Park M, Dargusch R, Fischer WH. F-spondin promotes nerve precursor differentiation. Journal of Neurochemistry 96: 444–453. 2006. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16300627. Accessed 11 February 2010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

