Small molecules targeted to a non-catalytic "RVxF" binding site of protein phosphatase-1 inhibit HIV-1
- PMID: 22768081
- PMCID: PMC3387161
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039481
Small molecules targeted to a non-catalytic "RVxF" binding site of protein phosphatase-1 inhibit HIV-1
Abstract
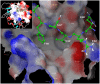
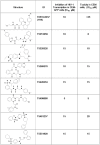
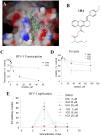
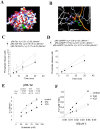
HIV-1 Tat protein recruits host cell factors including CDK9/cyclin T1 to HIV-1 TAR RNA and thereby induces HIV-1 transcription. An interaction with host Ser/Thr protein phosphatase-1 (PP1) is critical for this function of Tat. PP1 binds to a Tat sequence, Q(35)VCF(38), which resembles the PP1-binding "RVxF" motif present on PP1-binding regulatory subunits. We showed that expression of PP1 binding peptide, a central domain of Nuclear Inhibitor of PP1, disrupted the interaction of HIV-1 Tat with PP1 and inhibited HIV-1 transcription and replication. Here, we report small molecule compounds that target the "RVxF"-binding cavity of PP1 to disrupt the interaction of PP1 with Tat and inhibit HIV-1 replication. Using the crystal structure of PP1, we virtually screened 300,000 compounds and identified 262 small molecules that were predicted to bind the "RVxF"-accommodating cavity of PP1. These compounds were then assayed for inhibition of HIV-1 transcription in CEM T cells. One of the compounds, 1H4, inhibited HIV-1 transcription and replication at non-cytotoxic concentrations. 1H4 prevented PP1-mediated dephosphorylation of a substrate peptide containing an RVxF sequence in vitro. 1H4 also disrupted the association of PP1 with Tat in cultured cells without having an effect on the interaction of PP1 with the cellular regulators, NIPP1 and PNUTS, or on the cellular proteome. Finally, 1H4 prevented the translocation of PP1 to the nucleus. Taken together, our study shows that HIV- inhibition can be achieved through using small molecules to target a non-catalytic site of PP1. This proof-of-principle study can serve as a starting point for the development of novel antiviral drugs that target the interface of HIV-1 viral proteins with their host partners.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
1E7-03, a low MW compound targeting host protein phosphatase-1, inhibits HIV-1 transcription.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Nov;171(22):5059-75. doi: 10.1111/bph.12863. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25073485 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of a protein phosphatase 1 inhibitor, cdNIPP1, increases CDK9 threonine 186 phosphorylation and inhibits HIV-1 transcription.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 4;286(5):3798-804. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.196493. Epub 2010 Nov 22. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21098020 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by in silico screening targeting cyclin T1/Tat interaction.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Mar;57(3):1323-31. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01711-12. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23274668 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of HIV-1 transcription by protein phosphatase 1.Curr HIV Res. 2007 Jan;5(1):3-9. doi: 10.2174/157016207779316279. Curr HIV Res. 2007. PMID: 17266553 Review.
-
[Action of protein phosphatase-1 on Tat-dependent HIV-1 transcription and its related inhibitors].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2009 Dec;44(12):1343-7. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2009. PMID: 21351466 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Protein Phosphatase-1 Regulates Expression of Neuregulin-1.Biology (Basel). 2016 Dec 2;5(4):49. doi: 10.3390/biology5040049. Biology (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27918433 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Optimization of 2,3-Dihydro-1H-cyclopenta[b]quinolines Targeting the Noncatalytic RVxF Site of Protein Phosphatase 1 for HIV-1 Inhibition.ACS Infect Dis. 2020 Dec 11;6(12):3190-3211. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00511. Epub 2020 Dec 1. ACS Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33258581 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of the Protein Phosphatase 1 (PP1) in the context of viral infections.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jan 24;22(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01468-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38267954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The New Microtubule-Targeting Agent SIX2G Induces Immunogenic Cell Death in Multiple Myeloma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 6;23(18):10222. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810222. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142133 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Phosphatase 1-Targeting Small-Molecule C31 Inhibits Ebola Virus Replication.J Infect Dis. 2018 Nov 22;218(suppl_5):S627-S635. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiy422. J Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30169869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berkhout B, Silverman RH, Jeang KT. Tat trans-activates the human immunodeficiency virus through a nascent RNA target. Cell. 1989;59:273–282. - PubMed
-
- Nekhai S, Jeang KT. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of HIV-1 gene expression: role of cellular factors for Tat and Rev. Future Microbiol. 2006;1:417–426. - PubMed
-
- Ammosova T, Jerebtsova M, Beullens M, Voloshin Y, Ray PE, et al. Nuclear protein phosphatase-1 regulates HIV-1 transcription. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:32189–32194. - PubMed
-
- Washington K, Ammosova T, Beullens M, Jerebtsova M, Kumar A, et al. Protein phosphatase-1 dephosphorylates the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase-II. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:40442–40448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

