A common Ca2+-driven interdomain module governs eukaryotic NCX regulation
- PMID: 22768191
- PMCID: PMC3386913
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039985
A common Ca2+-driven interdomain module governs eukaryotic NCX regulation
Abstract
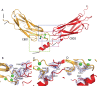
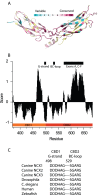
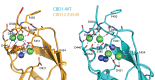
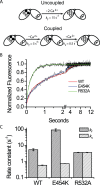
Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger (NCX) proteins mediate Ca(2+)-fluxes across the cell membrane to maintain Ca(2+) homeostasis in many cell types. Eukaryotic NCX contains Ca(2+)-binding regulatory domains, CBD1 and CBD2. Ca(2+) binding to a primary sensor (Ca3-Ca4 sites) on CBD1 activates mammalian NCXs, whereas CALX, a Drosophila NCX ortholog, displays an inhibitory response to regulatory Ca(2+). To further elucidate the underlying regulatory mechanisms, we determined the 2.7 Å crystal structure of mammalian CBD12-E454K, a two-domain construct that retains wild-type properties. In conjunction with stopped-flow kinetics and SAXS (small-angle X-ray scattering) analyses of CBD12 mutants, we show that Ca(2+) binding to Ca3-Ca4 sites tethers the domains via a network of interdomain salt-bridges. This Ca(2+)-driven interdomain switch controls slow dissociation of "occluded" Ca(2+) from the primary sensor and thus dictates Ca(2+) sensing dynamics. In the Ca(2+)-bound conformation, the interdomain angle of CBD12 is very similar in NCX and CALX, meaning that the interdomain distances cannot account for regulatory diversity in NCX and CALX. Since the two-domain interface is nearly identical among eukaryotic NCXs, including CALX, we suggest that the Ca(2+)-driven interdomain switch described here represents a general mechanism for initial conduction of regulatory signals in NCX variants.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular insights on CALX-CBD12 interdomain dynamics from MD simulations, RDCs, and SAXS.Biophys J. 2021 Sep 7;120(17):3664-3675. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2021.07.022. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Biophys J. 2021. PMID: 34310942 Free PMC article.
-
Population shift underlies Ca2+-induced regulatory transitions in the sodium-calcium exchanger (NCX).J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 9;288(32):23141-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.471698. Epub 2013 Jun 24. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23798674 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular determinants of allosteric regulation in NCX proteins.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;961:35-48. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4756-6_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224868 Review.
-
Dynamic features of allosteric Ca2+ sensor in tissue-specific NCX variants.Cell Calcium. 2012 Jun;51(6):478-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2012.04.007. Epub 2012 May 7. Cell Calcium. 2012. PMID: 22571864
-
Structural studies of the Ca(2+) regulatory domain of Drosophila Na(+)/Ca (2+) exchanger CALX.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;961:55-63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4756-6_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224870 Review.
Cited by
-
Sodium-calcium exchangers (NCX): molecular hallmarks underlying the tissue-specific and systemic functions.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Jan;466(1):43-60. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1405-y. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 24281864 Review.
-
Structure-based dynamic arrays in regulatory domains of sodium-calcium exchanger (NCX) isoforms.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 20;7(1):993. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01102-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28428550 Free PMC article.
-
Palmitoylation of the Na/Ca exchanger cytoplasmic loop controls its inactivation and internalization during stress signaling.FASEB J. 2015 Nov;29(11):4532-43. doi: 10.1096/fj.15-276493. Epub 2015 Jul 14. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 26174834 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insight into the allosteric inhibition of human sodium-calcium exchanger NCX1 by XIP and SEA0400.EMBO J. 2024 Jan;43(1):14-31. doi: 10.1038/s44318-023-00013-0. Epub 2023 Dec 15. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 38177313 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Based Function and Regulation of NCX Variants: Updates and Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 21;24(1):61. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010061. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613523 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Philipson KD, Nicoll DA. Sodium-calcium exchange: a molecular perspective. Annu Rev Physiol. 2000;62:111–133. - PubMed
-
- Blaustein MP, Lederer WJ. Sodium/calcium exchange: its physiological implications. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:763–854. - PubMed
-
- Lytton J. Na/Ca2+ exchangers: three mammalian gene families control Ca2+ transport. Biochem J. 2007;406:365–382. - PubMed
-
- Liao J, Li H, Zeng W, Sauer DB, Belmares R, et al. Structural insight into the ion-exchange mechanism of the sodium/calcium exchanger. Science. 2012;335:686–690. - PubMed
-
- Levitsky DO, Nicoll DA, Philipson KD. Identification of the high affinity Ca2+-binding domain of the cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:22847–22852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

