Extended JAK activation and delayed STAT1 dephosphorylation contribute to the distinct signaling profile of CNS neurons exposed to interferon-gamma
- PMID: 22769061
- PMCID: PMC3678282
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2012.06.006
Extended JAK activation and delayed STAT1 dephosphorylation contribute to the distinct signaling profile of CNS neurons exposed to interferon-gamma
Abstract
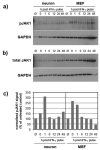
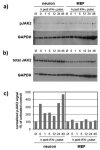
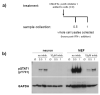
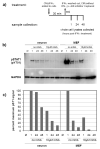
Although interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) plays a critical role in the noncytolytic elimination of many neurotropic viral infections, the signaling response to this cytokine has not been extensively characterized in primary CNS neurons. We previously demonstrated that the IFN-γ response at the signaling and gene expression levels is temporally extended in primary mouse hippocampal neurons, as compared to the transient response of primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF). We hypothesize that the protracted kinetics of STAT1 phosphorylation in IFN-γ-treated neurons are due to extended receptor activation and/or delayed STAT1 dephosphorylation in the nucleus. Here, we show that in response to IFN-γ, the Janus kinases (JAK1/JAK2) associated with the neuronal IFN-γ receptor complex remain active for an extended period as compared to MEF. Experimental inactivation of JAK1/JAK2 in neurons after IFN-γ treatment did not reverse the extended STAT1 phosphorylation phenotype. These results suggest that the extended kinetics of neuronal IFN-γ signaling are a product of distinct negative feedback mechanisms operating at both the receptor and within the nucleus.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unique aspects of IFN-γ/STAT1 signaling in neurons.Immunol Rev. 2022 Oct;311(1):187-204. doi: 10.1111/imr.13092. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Immunol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35656941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parafibromin Is a Component of IFN-γ-Triggered Signaling Pathways That Facilitates JAK1/2-Mediated Tyrosine Phosphorylation of STAT1.J Immunol. 2015 Sep 15;195(6):2870-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501111. Epub 2015 Jul 31. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26232434
-
Autophagy facilitates IFN-gamma-induced Jak2-STAT1 activation and cellular inflammation.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 10;285(37):28715-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.133355. Epub 2010 Jun 30. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20592027 Free PMC article.
-
STAT1-independent control of a neurotropic measles virus challenge in primary neurons and infected mice.J Immunol. 2012 Feb 15;188(4):1915-23. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101356. Epub 2012 Jan 13. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22246627 Free PMC article.
-
Prolactin enhances interferon-gamma-induced production of CXC ligand 9 (CXCL9), CXCL10, and CXCL11 in human keratinocytes.Endocrinology. 2007 May;148(5):2317-25. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-1639. Epub 2007 Jan 25. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17255201
Cited by
-
Unique aspects of IFN-γ/STAT1 signaling in neurons.Immunol Rev. 2022 Oct;311(1):187-204. doi: 10.1111/imr.13092. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Immunol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35656941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prolonged STAT1 activation in neurons drives a pathological transcriptional response.J Neuroimmunol. 2023 Sep 15;382:578168. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2023.578168. Epub 2023 Aug 2. J Neuroimmunol. 2023. PMID: 37556887 Free PMC article.
-
The antiviral cytokine interferon-gamma restricts neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation through activation of STAT1 and modulation of retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation.J Neurosci Res. 2017 Aug;95(8):1582-1601. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23987. Epub 2016 Nov 15. J Neurosci Res. 2017. PMID: 27862183 Free PMC article.
-
Covalently Immobilizing Interferon-γ Drives Filopodia Production through Specific Receptor-Ligand Interactions Independently of Canonical Downstream Signaling.Bioconjug Chem. 2020 May 20;31(5):1362-1369. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.0c00105. Epub 2020 May 11. Bioconjug Chem. 2020. PMID: 32329609 Free PMC article.
-
Bst2/Tetherin Is Induced in Neurons by Type I Interferon and Viral Infection but Is Dispensable for Protection against Neurotropic Viral Challenge.J Virol. 2015 Nov;89(21):11011-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01745-15. Epub 2015 Aug 26. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26311886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banker G, Goslin K. Culturing Nerve Cells. MIT Press; Cambridge: 1991.
-
- Chesler DA, Dodard C, Lee GY, Levy DE, Reiss CS. Interferon-gamma-induced inhibition of neuronal vesicular stomatitis virus infection is STAT1 dependent. J Neurovirol. 2004;10:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Darnell JE., Jr. STATs and gene regulation. Science. 1997;277:1630–1635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

