Scope of the palladium-catalyzed aryl borylation utilizing bis-boronic acid
- PMID: 22769742
- PMCID: PMC3407959
- DOI: 10.1021/ja303181m
Scope of the palladium-catalyzed aryl borylation utilizing bis-boronic acid
Abstract
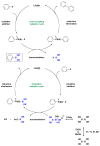
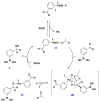
The Suzuki-Miyaura reaction has become one of the more useful tools for synthetic organic chemists. Until recently, there did not exist a direct way to make the most important component in the coupling reaction, namely the boronic acid. Current methods to make boronic acids often employ harsh or wasteful reagents to prepare boronic acid derivatives and require additional steps to afford the desired boronic acid. The scope of the previously reported palladium-catalyzed, direct boronic acid synthesis is unveiled, which includes a wide array of synthetically useful aryl electrophiles. It makes use of the newly available second generation Buchwald XPhos preformed palladium catalyst and bis-boronic acid. For ease of isolation and to preserve the often sensitive C-B bond, all boronic acids were readily converted to their more stable trifluoroborate counterparts.
Figures



References
-
- Bellina F, Carpita A, Rossi R. Synthesis. 2004:2419–2440.
-
- Kotha S, Lahiri K, Kashinath D. Tetrahedron. 2002;58:9633–9695.
-
- Carey JS, Laffan D, Thomson C, Williams MT. Org Biomol Chem. 2006;4:2337–2347. - PubMed
-
- Dugger RW, Ragan JA, Ripin DHB. Org Proc Res Dev. 2005;9:253–258.
-
- Cooper TWJ, Campbell IB, Macdonald SJF. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2010;49:8082–8091. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

