A translation-like cycle is a quality control checkpoint for maturing 40S ribosome subunits
- PMID: 22770215
- PMCID: PMC3615461
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.04.044
A translation-like cycle is a quality control checkpoint for maturing 40S ribosome subunits
Abstract
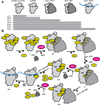
Assembly factors (AFs) prevent premature translation initiation on small (40S) ribosomal subunit assembly intermediates by blocking ligand binding. However, it is unclear how AFs are displaced from maturing 40S ribosomes, if or how maturing subunits are assessed for fidelity, and what prevents premature translation initiation once AFs dissociate. Here we show that maturation involves a translation-like cycle whereby the translation factor eIF5B, a GTPase, promotes joining of large (60S) subunits with pre-40S subunits to give 80S-like complexes, which are subsequently disassembled by the termination factor Rli1, an ATPase. The AFs Tsr1 and Rio2 block the mRNA channel and initiator tRNA binding site, and therefore 80S-like ribosomes lack mRNA or initiator tRNA. After Tsr1 and Rio2 dissociate from 80S-like complexes Rli1-directed displacement of 60S subunits allows for translation initiation. This cycle thus provides a functional test of 60S subunit binding and the GTPase site before ribosomes enter the translating pool.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

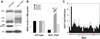



References
-
- Becker T, Armache JP, Jarasch A, Anger AM, Villa E, Sieber H, Motaal BA, Mielke T, Berninghausen O, Beckmann R. Structure of the no-go mRNA decay complex Dom34-Hbs1 bound to a stalled 80S ribosome. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011;18:715–720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

