Informatics methods to enable sharing of quantitative imaging research data
- PMID: 22770688
- PMCID: PMC3466343
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2012.04.007
Informatics methods to enable sharing of quantitative imaging research data
Abstract
Introduction: The National Cancer Institute Quantitative Research Network (QIN) is a collaborative research network whose goal is to share data, algorithms and research tools to accelerate quantitative imaging research. A challenge is the variability in tools and analysis platforms used in quantitative imaging. Our goal was to understand the extent of this variation and to develop an approach to enable sharing data and to promote reuse of quantitative imaging data in the community.
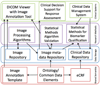
Methods: We performed a survey of the current tools in use by the QIN member sites for representation and storage of their QIN research data including images, image meta-data and clinical data. We identified existing systems and standards for data sharing and their gaps for the QIN use case. We then proposed a system architecture to enable data sharing and collaborative experimentation within the QIN.
Results: There are a variety of tools currently used by each QIN institution. We developed a general information system architecture to support the QIN goals. We also describe the remaining architecture gaps we are developing to enable members to share research images and image meta-data across the network.
Conclusions: As a research network, the QIN will stimulate quantitative imaging research by pooling data, algorithms and research tools. However, there are gaps in current functional requirements that will need to be met by future informatics development. Special attention must be given to the technical requirements needed to translate these methods into the clinical research workflow to enable validation and qualification of these novel imaging biomarkers.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Mia Levy - none
John Freymann- none
Justin Kirby - none
AndriyFedorov, PhD - none
Fiona Fennessy, MD, PhD - none
Steven Eschrich - none
Anders Berglund - none
David Fenstermacher - none
Yongqiang Tan- none
XiaotaoGuo- none
Thomas L. Casavant - none
Bartley Brown - none
Terry Braun - none
Andre Dekker
Erik Roelofs
James Mountz- none
Fernando Boada - none
Charles Laymon - none
Matt Oborski - none
Daniel Rubin - none
Figures
References
-
- Boulton G, Rawlins M, Vallance P, Walport M. Science as a public enterprise: the case for open data. [cited 2012 January 29];Lancet. 2011 May 14;377(9778):1633–1635. - PubMed
-
- Walport M, Brest P. Sharing research data to improve public health. [cited 2012 January 29];Lancet. 2011 Feb 12;377(9765):537–539. - PubMed
-
- Formerly PAR-08-225, now PAR-11-150. Available from: http://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/pa-files/PAR-11-150.html.
-
- Buckler AJ, Bresolin L, Dunnick NR, Sullivan DC, Aerts HJWL, Bendriem B, Bendtsen C, Boellaard R, Boone JM, Cole PE, et al. Quantitative imaging test approval and biomarker qualification: interrelated but distinct activities. [cited 2012 January 29];Radiology. 2011 Jun;259(3):875–884. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bogaerts J, Ford R, Sargent D, Schwartz LH, Rubinstein L, Lacombe D, Eisenhauer E, Verweij J, Therasse P. Individual patient data analysis to assess modifications to the RECIST criteria. [cited 2012 January 29];European Journal of Cancer (Oxford, England: 1990) 2009 Jan;45(2):248–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous