3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network
- PMID: 22770690
- PMCID: PMC3466397
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2012.05.001
3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network
Abstract
Quantitative analysis has tremendous but mostly unrealized potential in healthcare to support objective and accurate interpretation of the clinical imaging. In 2008, the National Cancer Institute began building the Quantitative Imaging Network (QIN) initiative with the goal of advancing quantitative imaging in the context of personalized therapy and evaluation of treatment response. Computerized analysis is an important component contributing to reproducibility and efficiency of the quantitative imaging techniques. The success of quantitative imaging is contingent on robust analysis methods and software tools to bring these methods from bench to bedside. 3D Slicer is a free open-source software application for medical image computing. As a clinical research tool, 3D Slicer is similar to a radiology workstation that supports versatile visualizations but also provides advanced functionality such as automated segmentation and registration for a variety of application domains. Unlike a typical radiology workstation, 3D Slicer is free and is not tied to specific hardware. As a programming platform, 3D Slicer facilitates translation and evaluation of the new quantitative methods by allowing the biomedical researcher to focus on the implementation of the algorithm and providing abstractions for the common tasks of data communication, visualization and user interface development. Compared to other tools that provide aspects of this functionality, 3D Slicer is fully open source and can be readily extended and redistributed. In addition, 3D Slicer is designed to facilitate the development of new functionality in the form of 3D Slicer extensions. In this paper, we present an overview of 3D Slicer as a platform for prototyping, development and evaluation of image analysis tools for clinical research applications. To illustrate the utility of the platform in the scope of QIN, we discuss several use cases of 3D Slicer by the existing QIN teams, and we elaborate on the future directions that can further facilitate development and validation of imaging biomarkers using 3D Slicer.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

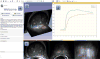
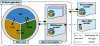


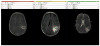
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2011;61(2):69–90. - PubMed
-
- Park JW, Kerbel RS, Kelloff GJ, Barrett JC, Chabner Ba, Parkinson DR, Peck J, Ruddon RW, Sigman CC, Slamon DJ. Rationale for biomarkers and surrogate end points in mechanism-driven oncology drug development. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2004 Jun 1;10(11):3885–96. - PubMed
-
- Eisenhauer E, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz L, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1) European journal of cancer (Oxford, England: 1990) 2009 Jan;45(2):228–247. - PubMed
-
- Jaffe Ta, Wickersham NW, Sullivan DC. Quantitative imaging in oncology patients: Part 1, radiology practice patterns at major U.S. cancer centers. AJR American journal of roentgenology. 2010 Jul;195(1):101–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01-CA140206/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54EB005149/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA140206/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB004640/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA151261/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01CA154601-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA111288/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA154601/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41EB015898/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P41RR13218/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA151261/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 EB005149/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR019703/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R00 LM009889/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015898/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR013218/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA154602/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 4R00LM009889-03/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01CA111288/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

