The mouse Wnt/PCP protein Vangl2 is necessary for migration of facial branchiomotor neurons, and functions independently of Dishevelled
- PMID: 22771245
- PMCID: PMC3484895
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.06.021
The mouse Wnt/PCP protein Vangl2 is necessary for migration of facial branchiomotor neurons, and functions independently of Dishevelled
Abstract
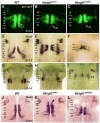
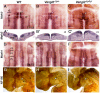
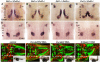
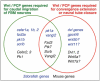
During development, facial branchiomotor (FBM) neurons, which innervate muscles in the vertebrate head, migrate caudally and radially within the brainstem to form a motor nucleus at the pial surface. Several components of the Wnt/planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway, including the transmembrane protein Vangl2, regulate caudal migration of FBM neurons in zebrafish, but their roles in neuronal migration in mouse have not been investigated in detail. Therefore, we analyzed FBM neuron migration in mouse looptail (Lp) mutants, in which Vangl2 is inactivated. In Vangl2(Lp/+) and Vangl2(Lp/Lp) embryos, FBM neurons failed to migrate caudally from rhombomere (r) 4 into r6. Although caudal migration was largely blocked, many FBM neurons underwent normal radial migration to the pial surface of the neural tube. In addition, hindbrain patterning and FBM progenitor specification were intact, and FBM neurons did not transfate into other non-migratory neuron types, indicating a specific effect on caudal migration. Since loss-of-function in some zebrafish Wnt/PCP genes does not affect caudal migration of FBM neurons, we tested whether this was also the case in mouse. Embryos null for Ptk7, a regulator of PCP signaling, had severe defects in caudal migration of FBM neurons. However, FBM neurons migrated normally in Dishevelled (Dvl) 1/2 double mutants, and in zebrafish embryos with disrupted Dvl signaling, suggesting that Dvl function is essentially dispensable for FBM neuron caudal migration. Consistent with this, loss of Dvl2 function in Vangl2(Lp/+) embryos did not exacerbate the Vangl2(Lp/+) neuronal migration phenotype. These data indicate that caudal migration of FBM neurons is regulated by multiple components of the Wnt/PCP pathway, but, importantly, may not require Dishevelled function. Interestingly, genetic-interaction experiments suggest that rostral FBM neuron migration, which is normally suppressed, depends upon Dvl function.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The PCP protein Vangl2 regulates migration of hindbrain motor neurons by acting in floor plate cells, and independently of cilia function.Dev Biol. 2013 Oct 15;382(2):400-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.08.017. Epub 2013 Aug 26. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23988578 Free PMC article.
-
Prickle1 is necessary for the caudal migration of murine facial branchiomotor neurons.Cell Tissue Res. 2014 Sep;357(3):549-61. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-1925-6. Epub 2014 Jun 15. Cell Tissue Res. 2014. PMID: 24927917 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt activity guides facial branchiomotor neuron migration, and involves the PCP pathway and JNK and ROCK kinases.Neural Dev. 2009 Feb 11;4:7. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-4-7. Neural Dev. 2009. PMID: 19210786 Free PMC article.
-
Facial motor neuron migration advances.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013 Dec;23(6):943-50. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Sep 30. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 24090878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moving cell bodies: understanding the migratory mechanism of facial motor neurons.Arch Pharm Res. 2007 Oct;30(10):1273-82. doi: 10.1007/BF02980268. Arch Pharm Res. 2007. PMID: 18038906 Review.
Cited by
-
Defective Neuronal Positioning Correlates With Aberrant Motor Circuit Function in Zebrafish.Front Neural Circuits. 2021 Jun 24;15:690475. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2021.690475. eCollection 2021. Front Neural Circuits. 2021. PMID: 34248505 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of germline VANGL2 variants using rescue assays of vangl2 knockout zebrafish.Hum Mol Genet. 2024 Jan 7;33(2):150-169. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddad171. Hum Mol Genet. 2024. PMID: 37815931 Free PMC article.
-
The planar cell polarity protein VANG-1/Vangl negatively regulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling through a Dvl dependent mechanism.PLoS Genet. 2018 Dec 7;14(12):e1007840. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007840. eCollection 2018 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30532125 Free PMC article.
-
Vangl2 cooperates with Rab11 and Myosin V to regulate apical constriction during vertebrate gastrulation.Development. 2015 Jan 1;142(1):99-107. doi: 10.1242/dev.111161. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Development. 2015. PMID: 25480917 Free PMC article.
-
Motor neuron cell bodies are actively positioned by Slit/Robo repulsion and Netrin/DCC attraction.Dev Biol. 2015 Mar 1;399(1):68-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.12.014. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25530182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carpenter EM, Goddard JM, Chisaka O, Manley NR, Capecchi MR. Loss of Hox-A1 (Hox-1.6) function results in the reorganization of the murine hindbrain. Development. 1993;118:1063–75. - PubMed
-
- Carreira-Barbosa F, Concha ML, Takeuchi M, Ueno N, Wilson SW, Tada M. Prickle 1 regulates cell movements during gastrulation and neuronal migration in zebrafish. Development. 2003;130:4037–46. - PubMed
-
- Chandrasekhar A, Moens CB, Warren JT, Jr., Kimmel CB, Kuwada JY. Development of branchiomotor neurons in zebrafish. Development. 1997;124:2633–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

