Two independent forms of activity-dependent potentiation regulate electrical transmission at mixed synapses on the Mauthner cell
- PMID: 22771708
- PMCID: PMC4102419
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.05.059
Two independent forms of activity-dependent potentiation regulate electrical transmission at mixed synapses on the Mauthner cell
Abstract
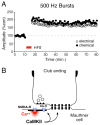
Mixed (electrical and chemical) synaptic contacts on the Mauthner cells, known as Club endings, constitute a valuable model for the study of vertebrate electrical transmission. While electrical synapses are still perceived by many as passive intercellular channels that lack modifiability, a wealth of experimental evidence shows that gap junctions at Club endings are subject to dynamic regulatory control by two independent activity-dependent mechanisms that lead to potentiation of electrical transmission. One of those mechanisms relies on activation of NMDA receptors and postsynaptic CaMKII. A second mechanism relies on mGluR activation and endocannabinoid production and is indirectly mediated via the release of dopamine from nearby varicosities, which in turn leads to potentiation of the synaptic response via a PKA-mediated postsynaptic mechanism. We review here these two forms of potentiation and their signaling mechanisms, which include the activation of two kinases with well-established roles as regulators of synaptic strength, as well as the functional implications of these two forms of potentiation. Special Issue entitled Electrical Synapses.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Alev C, Urschel S, Sonntag S, Zoidl G, Fort AG, Höher T, Matsubara M, Willecke K, Spray DC, Dermietzel R. The neuronal connexin36 interacts with and is phosphorylated by CaMKII in a way similar to CaMKII interaction with glutamate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:20964–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alger BE. Retrograde signaling in the regulation of synaptic transmission: focus on endocannabinoids. Prog Neurobiol. 2002;68:247–86. - PubMed
-
- Barria A, Muller D, Derkach V, Griffith LC, Soderling TR. Regulatory phosphorylation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors by CaM-KII during long-term potentiation. Science. 1997;276:2042–5. - PubMed
-
- Bartelmez GW. Mauthner's cell and the nucleus motorius tegmenti. The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1915;25:87–128.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

