A phosphoenol pyruvate phosphatase transcript is induced in the root nodule cortex of Phaseolus vulgaris under conditions of phosphorus deficiency
- PMID: 22771853
- PMCID: PMC3428000
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/ers151
A phosphoenol pyruvate phosphatase transcript is induced in the root nodule cortex of Phaseolus vulgaris under conditions of phosphorus deficiency
Abstract
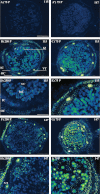
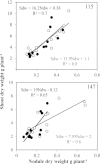
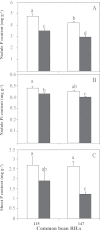
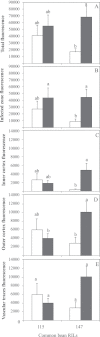
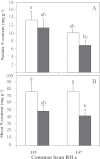
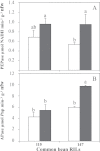
Although previous studies on N2-fixing legumes have demonstrated the contribution of acid phosphatases to their phosphorus (P) use efficiency under P-deficient growth conditions, localization of these enzymes in bean nodules has not been demonstrated. In this study, phosphoenol pyruvate phosphatase (PEPase) gene transcripts were localized within the nodule tissues of two recombinant inbred lines, RIL115 (P-deficiency tolerant) and RIL147 (P-deficiency sensitive), of Phaseolus vulgaris. Nodules were induced by Rhizobium tropici CIAT899 under hydroaeroponic conditions with a sufficient versus a deficient P supply. The results indicated that PEPase transcripts were particularly abundant in the nodule infected zone and cortex of both RILs. Analysis of fluorescence intensity indicated that nodule PEPase was induced under conditions of P deficiency to a significantly higher extent in RIL147 than in RIL115, and more in the inner cortex (91%) than in the outer cortex (71%) or the infected zone (79%). In addition, a significant increase (39%) in PEPase enzyme activity in the P-deficient RIL147 correlated with an increase (58%) in the efficiency of use in rhizobial symbiosis. It was concluded that nodule PEPase is upregulated under conditions of P deficiency in the P-deficiency-sensitive RIL147, and that this gene may contribute to adaptation of rhizobial symbiosis to low-P environments.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential expression of trehalose 6-P phosphatase and ascorbate peroxidase transcripts in nodule cortex of Phaseolus vulgaris and regulation of nodule O2 permeability.Planta. 2013 Jul;238(1):107-19. doi: 10.1007/s00425-013-1877-1. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Planta. 2013. PMID: 23575967
-
A phytase gene is overexpressed in root nodules cortex of Phaseolus vulgaris-rhizobia symbiosis under phosphorus deficiency.Planta. 2013 Aug;238(2):317-24. doi: 10.1007/s00425-013-1893-1. Epub 2013 May 16. Planta. 2013. PMID: 23677567
-
Expression of a phosphate-starvation inducible fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase gene in common bean nodules correlates with phosphorus use efficiency.J Plant Physiol. 2016 Oct 20;205:48-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2016.08.013. Epub 2016 Sep 9. J Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27614785
-
Specific expression and activity of acid phosphatases in common bean nodules.Plant Signal Behav. 2013 Aug;8(8):e25022. doi: 10.4161/psb.25022. Epub 2013 May 17. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23733065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The nodule conductance to O₂ diffusion increases with phytase activity in N₂-fixing Phaseolus vulgaris L.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014 Jul;80:53-9. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.03.023. Epub 2014 Apr 1. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24727788
Cited by
-
Differential expression of trehalose 6-P phosphatase and ascorbate peroxidase transcripts in nodule cortex of Phaseolus vulgaris and regulation of nodule O2 permeability.Planta. 2013 Jul;238(1):107-19. doi: 10.1007/s00425-013-1877-1. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Planta. 2013. PMID: 23575967
-
Phosphate Solubilizing Rhizobacteria Could Have a Stronger Influence on Wheat Root Traits and Aboveground Physiology Than Rhizosphere P Solubilization.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Jul 10;11:979. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00979. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32765544 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome Analysis of the Soybean Nodule Phosphorus Response Mechanism and Characterization of Stress-Induced Ribosome Structural and Protein Expression Changes.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 9;13:908889. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.908889. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35755677 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfur-enriched leonardite and humic acid soil amendments enhance tolerance to drought and phosphorus deficiency stress in maize (Zea mays L.).Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 14;10(1):6432. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62669-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32286357 Free PMC article.
-
GmEXPB2, a Cell Wall β-Expansin, Affects Soybean Nodulation through Modifying Root Architecture and Promoting Nodule Formation and Development.Plant Physiol. 2015 Dec;169(4):2640-53. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01029. Epub 2015 Oct 2. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26432877 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AFNOR (1969). Dosage spectrophotométrique de l’anhydride phosphorique: méthode vanadomolybdique Paris: : AFNOR; 224 246
-
- Araújo AP, Plassard C, Drevon JJ. Phosphatase and phytase activities in nodules of common bean genotypes at different levels of phosphorus supply. Plant and Soil. 2008;312:129–138.
-
- Bargaz A, Drevon JJ, Oufdou K, Mandri B, Faghire M, Ghoulam C. Nodule phosphorus requirement and O2 uptake in common bean genotypes under phosphorus deficiency. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica B Soil and Plant Sciences. 2011a;61:602–611.
-
- Bargaz A, Ghoulam C, Faghire M, Aslan Attar H, Drevon JJ. The nodule conductance to the O2 diffusion increases with high phosphorus content in the Phaseolus vulgaris–rhizobia symbiosis. Symbiosis. 2011b;53:157–164.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

