Role of host cell factor-1 in cell cycle regulation
- PMID: 22771988
- PMCID: PMC3654768
- DOI: 10.4161/trns.20711
Role of host cell factor-1 in cell cycle regulation
Abstract
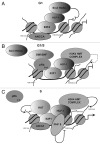
Host cell factor-1(HCF-1) was first discovered as a cellular cofactor in the VP16-induced complex, a multi-protein DNA complex that forms on immediate early gene promoters of herpes simplex virus (HSV) to activate viral gene transcription. Subsequent research has revealed HCF-1 to be an abundant chromatin-associated protein that regulates various stages of the cell cycle. Recent reports show that HCF-1 interacts with diverse E2F proteins to induce cell-cycle-specific transcription. HCF-1 can act as a scaffold to a variety of histone-modifying proteins and these HCF-1-E2F-containing multi-protein complexes can bring about context-dependent activation or repression of transcription. In this review we examine the diversity of HCF-E2F interactions and the variety of multi-protein complexes it occurs in, to influence the local chromatin landscape at the E2F-promoters.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
