Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: results of a randomised placebo-controlled trial (ABILITY-1)
- PMID: 22772328
- PMCID: PMC3664374
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201766
Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: results of a randomised placebo-controlled trial (ABILITY-1)
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA).
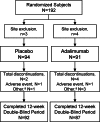
Methods: Patients fulfilled Assessment of Spondyloarthritis international Society (ASAS) criteria for axial spondyloarthritis, had a Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) score of ≥ 4, total back pain score of ≥ 4 (10 cm visual analogue scale) and inadequate response, intolerance or contraindication to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs); patients fulfilling modified New York criteria for ankylosing spondylitis were excluded. Patients were randomised to adalimumab (N=91) or placebo (N=94). The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients achieving ASAS40 at week 12. Efficacy assessments included BASDAI and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS). MRI was performed at baseline and week 12 and scored using the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) index.
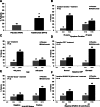
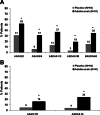
Results: Significantly more patients in the adalimumab group achieved ASAS40 at week 12 compared with patients in the placebo group (36% vs 15%, p<0.001). Significant clinical improvements based on other ASAS responses, ASDAS and BASDAI were also detected at week 12 with adalimumab treatment, as were improvements in quality of life measures. Inflammation in the spine and sacroiliac joints on MRI significantly decreased after 12 weeks of adalimumab treatment. Shorter disease duration, younger age, elevated baseline C-reactive protein or higher SPARCC MRI sacroiliac joint scores were associated with better week 12 responses to adalimumab. The safety profile was consistent with what is known for adalimumab in ankylosing spondylitis and other diseases.
Conclusions: In patients with nr-axSpA, adalimumab treatment resulted in effective control of disease activity, decreased inflammation and improved quality of life compared with placebo. Results from ABILITY-1 suggest that adalimumab has a positive benefit-risk profile in active nr-axSpA patients with inadequate response to NSAIDs.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00939003.
Figures
Comment in
-
Treatment of non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: it is only the beginning.Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 Jun;72(6):789-90. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202908. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013. PMID: 23667168 No abstract available.
-
Anti-TNF response rates in radiographic and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthropathy.Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Mar;74(3):e21. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206811. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 25371443 No abstract available.
References
-
- van der Linden S, Valkenburg H, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis: a proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 1984;27:361–8 - PubMed
-
- Rudwaleit M, Khan MA, Sieper J. The challenge of diagnosis and classification in early ankylosing spondylitis: do we need new criteria? Arthritis Rheum 2005;52:1000–8 - PubMed
-
- Weber U, Lambert RG, Ostergaard M, et al. The diagnostic utility of magnetic resonance imaging in spondylarthritis: an international multicenter evaluation of one hundred eighty-seven subjects. Arthritis Rheum 2010;62:3048–58 - PubMed
-
- Rudwaleit M, Landewe R, van der Heijde D, et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part I): classification of paper patients by expert opinion including uncertainty appraisal. Ann Rheum Dis 2009;68:770–6 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

