TGFB2 mutations cause familial thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections associated with mild systemic features of Marfan syndrome
- PMID: 22772371
- PMCID: PMC4033668
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2348
TGFB2 mutations cause familial thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections associated with mild systemic features of Marfan syndrome
Abstract
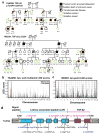
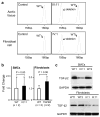
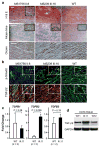
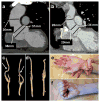
A predisposition for thoracic aortic aneurysms leading to acute aortic dissections can be inherited in families in an autosomal dominant manner. Genome-wide linkage analysis of two large unrelated families with thoracic aortic disease followed by whole-exome sequencing of affected relatives identified causative mutations in TGFB2. These mutations-a frameshift mutation in exon 6 and a nonsense mutation in exon 4-segregated with disease with a combined logarithm of odds (LOD) score of 7.7. Sanger sequencing of 276 probands from families with inherited thoracic aortic disease identified 2 additional TGFB2 mutations. TGFB2 encodes transforming growth factor (TGF)-β2, and the mutations are predicted to cause haploinsufficiency for TGFB2; however, aortic tissue from cases paradoxically shows increased TGF-β2 expression and immunostaining. Thus, haploinsufficiency for TGFB2 predisposes to thoracic aortic disease, suggesting that the initial pathway driving disease is decreased cellular TGF-β2 levels leading to a secondary increase in TGF-β2 production in the diseased aorta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Transforming growth factor β2 mutations and familial thoracic aortic aneurysms.Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2012 Oct 1;5(5):593-4. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.112.964858. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2012. PMID: 23074340 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hiratzka LF, et al. 2010 ACCF/AHA/AATS/ACR/ASA/SCA/SCAI/SIR/STS/SVM Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Patients With Thoracic Aortic Disease: Executive Summary. A Report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American College of Radiology, American Stroke Association, Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology, Society of Thoracic Surgeons, and Society for Vascular Medicine. Circulation. 2010;121:e266–369. - PubMed
-
- Faivre L, et al. Pathogenic FBN1 mutations in 146 adults not meeting clinical diagnostic criteria for Marfan syndrome: further delineation of type 1 fibrillinopathies and focus on patients with an isolated major criterion. Am J Med Genet A. 2009;149A:854–860. - PubMed
-
- Loeys BL, et al. Aneurysm syndromes caused by mutations in the TGF-beta receptor. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:788–798. - PubMed
-
- van de Laar IM, et al. Mutations in SMAD3 cause a syndromic form of aortic aneurysms and dissections with early-onset osteoarthritis. Nat Genet. 2011;43:121–126. - PubMed
-
- Gomez D, et al. Syndromic and non-syndromic aneurysms of the human ascending aorta share activation of the Smad2 pathway. J Pathol. 2009;218:131–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UC2 HL103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL062594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HL109942/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024148/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50HL083794-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL62594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL083794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

