Ultraviolet radiation damages self noncoding RNA and is detected by TLR3
- PMID: 22772463
- PMCID: PMC3812946
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2861
Ultraviolet radiation damages self noncoding RNA and is detected by TLR3
Abstract
Exposure to ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation from the sun can result in sunburn, premature aging and carcinogenesis, but the mechanism responsible for acute inflammation of the skin is not well understood. Here we show that RNA is released from keratinocytes after UVB exposure and that this stimulates production of the inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) from nonirradiated keratinocytes and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Whole-transcriptome sequencing revealed that UVB irradiation of keratinocytes induced alterations in the double-stranded domains of some noncoding RNAs. We found that this UVB-damaged RNA was sufficient to induce cytokine production from nonirradiated cells, as UVB irradiation of a purified noncoding RNA (U1 RNA) reproduced the same response as the one we observed to UVB-damaged keratinocytes. The responses to both UVB-damaged self-RNAs and UVB-damaged keratinocytes were dependent on Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) and Toll-like receptor adaptor molecule 1 (TRIF). In response to UVB exposure, Tlr3(-/-) mice did not upregulate TNF-α in the skin. Moreover, TLR3 was also necessary for UVB-radiation-induced immune suppression. These findings establish that UVB damage is detected by TLR3 and that self-RNA is a damage-associated molecular pattern that serves as an endogenous signal of solar injury.
Figures
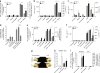
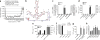
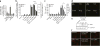
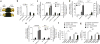
References
-
- Armstrong BK, Kricker A. The epidemiology of UV induced skin cancer. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2001;63:8–18. - PubMed
-
- El Ghissassi F, et al. A review of human carcinogens–part D: radiation. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:751–752. - PubMed
-
- Sontag Y, et al. Cells with UV-specifc DNA damage are present in murine lymph nodes after in vivo UV irradiation. J Invest Dermatol. 1995;104:734–738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 AI052453/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES007148/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES005022/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- AR48805/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR056667/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI0833358/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI083358/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI052453/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR056667/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL107150/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR052728/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR052728/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- ES007148/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- ES005022/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI052453/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

