Regional infant brain development: an MRI-based morphometric analysis in 3 to 13 month olds
- PMID: 22772652
- PMCID: PMC3729199
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhs197
Regional infant brain development: an MRI-based morphometric analysis in 3 to 13 month olds
Abstract
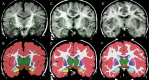
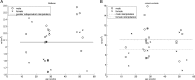
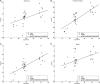
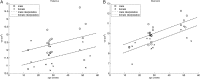
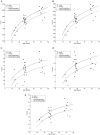
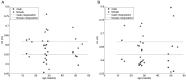
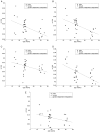
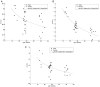
Elucidation of infant brain development is a critically important goal given the enduring impact of these early processes on various domains including later cognition and language. Although infants' whole-brain growth rates have long been available, regional growth rates have not been reported systematically. Accordingly, relatively less is known about the dynamics and organization of typically developing infant brains. Here we report global and regional volumetric growth of cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem with gender dimorphism, in 33 cross-sectional scans, over 3 to 13 months, using T1-weighted 3-dimensional spoiled gradient echo images and detailed semi-automated brain segmentation. Except for the midbrain and lateral ventricles, all absolute volumes of brain regions showed significant growth, with 6 different patterns of volumetric change. When normalized to the whole brain, the regional increase was characterized by 5 differential patterns. The putamen, cerebellar hemispheres, and total cerebellum were the only regions that showed positive growth in the normalized brain. Our results show region-specific patterns of volumetric change and contribute to the systematic understanding of infant brain development. This study greatly expands our knowledge of normal development and in future may provide a basis for identifying early deviation above and beyond normative variation that might signal higher risk for neurological disorders.
Keywords: MRI; brain development; infant; volumetric analysis.
Figures





References
-
- Barkovich AJ. Magnetic resonance techniques in the assessment of myelin and myelination. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2005;28(3):311–343. doi:10.1007/s10545-005-5952-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bohbot VD, Kalina M, Stepankova K, Spackova N, Petrides M, Nadel L. Spatial memory deficits in patients with lesions to the right hippocampus and to the right parahippocampal cortex. Neuropsychologia. 1998;36:1217–1238. doi:10.1016/S0028-3932(97)00161-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Burgess N, Maguire EA, O'Keefe J. The human hippocampus and spatial and episodic memory. Neuron. 2002;35:625–641. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00830-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Castellanos FX, Giedd JN, Marsh WL, Hamburger SD, Vaituzis AC, Dickstein DP, Sarfatti SE, Vauss YC, Snell JW, Lange N, et al. Quantitative brain magnetic resonance imaging in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1996;53(7):607–616. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1996.01830070053009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

