Gene silencing in tick cell lines using small interfering or long double-stranded RNA
- PMID: 22773071
- PMCID: PMC3557390
- DOI: 10.1007/s10493-012-9598-x
Gene silencing in tick cell lines using small interfering or long double-stranded RNA
Abstract
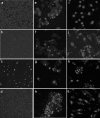
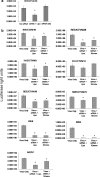
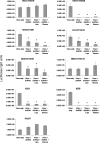
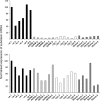
Gene silencing by RNA interference (RNAi) is an important research tool in many areas of biology. To effectively harness the power of this technique in order to explore tick functional genomics and tick-microorganism interactions, optimised parameters for RNAi-mediated gene silencing in tick cells need to be established. Ten cell lines from four economically important ixodid tick genera (Amblyomma, Hyalomma, Ixodes and Rhipicephalus including the sub-species Boophilus) were used to examine key parameters including small interfering RNA (siRNA), double stranded RNA (dsRNA), transfection reagent and incubation time for silencing virus reporter and endogenous tick genes. Transfection reagents were essential for the uptake of siRNA whereas long dsRNA alone was taken up by most tick cell lines. Significant virus reporter protein knockdown was achieved using either siRNA or dsRNA in all the cell lines tested. Optimum conditions varied according to the cell line. Consistency between replicates and duration of incubation with dsRNA were addressed for two Ixodes scapularis cell lines; IDE8 supported more consistent and effective silencing of the endogenous gene subolesin than ISE6, and highly significant knockdown of the endogenous gene 2I1F6 in IDE8 cells was achieved within 48 h incubation with dsRNA. In summary, this study shows that gene silencing by RNAi in tick cell lines is generally more efficient with dsRNA than with siRNA but results vary between cell lines and optimal parameters need to be determined for each experimental system.
Figures
References
-
- Attarzadeh-Yazdi G, Fragkoudis R, Chi Y, Siu RW, Ulper L, Barry G, Rodriguez-Andres J, Nash AA, Bouloy M, Merits A, Fazakerley JK, Kohl A. Cell-to-cell spread of the RNA interference response suppresses Semliki Forest virus (SFV) infection of mosquito cell cultures and cannot be antagonized by SFV. J Virol. 2009;83:5735–5748. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02440-08. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barnard A-C, Nijhof AM, Gaspar ARM, Neitz AWH, Jongejan F, Maritz-Olivier C. Expression profiling, gene silencing and transcriptional networking of metzincin metalloproteases in the cattle tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Vet Parasitol. 2012;186:403–414. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.11.026. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

