The bacterium Pantoea stewartii uses two different type III secretion systems to colonize its plant host and insect vector
- PMID: 22773631
- PMCID: PMC3416588
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00892-12
The bacterium Pantoea stewartii uses two different type III secretion systems to colonize its plant host and insect vector
Abstract
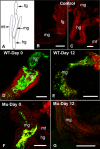
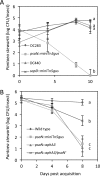
Plant- and animal-pathogenic bacteria utilize phylogenetically distinct type III secretion systems (T3SS) that produce needle-like injectisomes or pili for the delivery of effector proteins into host cells. Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii (herein referred to as P. stewartii), the causative agent of Stewart's bacterial wilt and leaf blight of maize, carries phylogenetically distinct T3SSs. In addition to an Hrc-Hrp T3SS, known to be essential for maize pathogenesis, P. stewartii has a second T3SS (Pantoea secretion island 2 [PSI-2]) that is required for persistence in its flea beetle vector, Chaetocnema pulicaria (Melsh). PSI-2 belongs to the Inv-Mxi-Spa T3SS family, typically found in animal pathogens. Mutagenesis of the PSI-2 psaN gene, which encodes an ATPase essential for secretion of T3SS effectors by the injectisome, greatly reduces both the persistence of P. stewartii in flea beetle guts and the beetle's ability to transmit P. stewartii to maize. Ectopic expression of the psaN gene complements these phenotypes. In addition, the PSI-2 psaN gene is not required for P. stewartii pathogenesis of maize and is transcriptionally upregulated in insects compared to maize tissues. Thus, the Hrp and PSI-2 T3SSs play different roles in the life cycle of P. stewartii as it alternates between its insect vector and plant host.
Figures




References
-
- Ammar ED, Hogenhout SA. 2008. A neurotropic route for Maize mosaic virus (Rhabdoviridae) in its planthopper vector Peregrinus maidis. Virus Res. 131: 77–85 - PubMed
-
- Blocker A, et al. 2001. Structure and composition of the Shigella flexneri “needle complex”, a part of its type III secreton. Mol. Microbiol. 39: 652–663 - PubMed
-
- Boyer HW, Roulland-Dussoix D. 1969. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 41: 459–472 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

