Sequential in-office vitreous aspirates demonstrate vitreous matrix metalloproteinase 9 levels correlate with the amount of subretinal fluid in eyes with wet age-related macular degeneration
- PMID: 22773904
- PMCID: PMC3388986
Sequential in-office vitreous aspirates demonstrate vitreous matrix metalloproteinase 9 levels correlate with the amount of subretinal fluid in eyes with wet age-related macular degeneration
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate levels of 37 native pathway proteins of the vitreous proteome from a subset of wet age-related macular degeneration (AMD) patients with and without subretinal fluid (SRF).
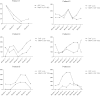
Methods: A total of 62 consecutive samples were aspirated from 12 patients with AMD, six who had SRF at baseline, and six who did not have SRF at any point during the study. Vitreous levels of the 37 native pathway proteins were analyzed in these patients using reverse phase protein microarray technology. At each visit, at which the 62 samples were taken, SRF and central retinal thickness were measured. These values were then compared to the relative intensity level of the 37 proteins screened.
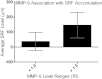
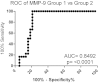
Results: In the subset of AMD patients with SRF, the average matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9), interleukin (IL)-12, Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1 (cABL) Thr735, heme oxygenase-1, Musashi, platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta Tyr751 (PDGFRβ), IL-8, and BCL-2 associated death promoter (BAD) Ser112 levels in the vitreous were found to be significantly different with a 21%-82% increase in expression compared to those without SRF (p<0.0001). Within the SRF group, there was a positive correlation between the vitreous MMP-9 levels and the SRF level. MMP-9 levels in the vitreous proteome varied with the level of SRF but not retinal edema. Compared to patients without SRF, the patients with initial SRF had persistent or progressive disease.
Conclusions: This is the first prospective case series sequentially monitoring the vitreous proteome in patients with wet AMD. The results suggest that MMP-9 is a proteomic biomarker of SRF accumulation, separate from macular edema.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of interleukin-6 and matrix metalloproteinase expression in the subretinal fluid and the vitreous during proliferative vitreoretinopathy: correlations with extent, duration of RRD and PVR grade.Cytokine. 2014 Jun;67(2):71-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2014.02.012. Epub 2014 Mar 29. Cytokine. 2014. PMID: 24725542
-
Analyses of the effects of persistent subretinal fluid on visual/anatomic outcomes according to the type of macular neovascularization during the relaxed treat-and-extend protocol in age-related macular degeneration patients.BMC Ophthalmol. 2021 Aug 10;21(1):294. doi: 10.1186/s12886-021-02063-6. BMC Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34376158 Free PMC article.
-
Activated VEGF receptor shed into the vitreous in eyes with wet AMD: a new class of biomarkers in the vitreous with potential for predicting the treatment timing and monitoring response.Arch Ophthalmol. 2009 May;127(5):613-21. doi: 10.1001/archophthalmol.2009.88. Arch Ophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 19433709 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the correlation of lymphangiogenesis biomarkers with clinical condition in Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD).Exp Eye Res. 2024 Jun;243:109891. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2024.109891. Epub 2024 Apr 13. Exp Eye Res. 2024. PMID: 38615832
-
Association analysis of genetic polymorphisms and expression levels of selected genes involved in extracellular matrix turnover and angiogenesis with the risk of age-related macular degeneration.Ophthalmic Genet. 2018 Dec;39(6):684-698. doi: 10.1080/13816810.2018.1525752. Epub 2018 Oct 5. Ophthalmic Genet. 2018. PMID: 30289322
Cited by
-
Ranibizumab Modifies the Expression of Metalloproteinases and Their Tissue Inhibitors in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Patients with Exudative Age-Related Macular Degeneration.J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 4;13(1):295. doi: 10.3390/jcm13010295. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38202302 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics of vitreous humor of patients with exudative age-related macular degeneration.PLoS One. 2014 May 14;9(5):e96895. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096895. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24828575 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Biomarkers of Retinal Inflammation in Diabetic Retinopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 25;20(19):4755. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194755. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31557880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety and Feasibility of Quantitative Multiplexed Cytokine Analysis From Office-Based Vitreous Aspiration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Jun 1;57(7):3017-23. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-18721. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27273720 Free PMC article.
-
Disturbed Matrix Metalloproteinases Activity in Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1415:21-26. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-27681-1_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37440009 Review.
References
-
- Guymer RH, Tao LW, Goh JK, Liew D, Ischenko O, Robman LD, Aung K, Cipriani T, Cain M, Richardson AJ, Baird PN, Langham R. Identification of Urinary Biomarkers for Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:4639–44. - PubMed
-
- Seddon JM, George S, Rosner B, Rifai N. Progression of Age-Related Macular Degeneration Prospective Assessment of C-Reactive Protein, Interleukin 6, and Other Cardiovascular Biomarkers. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005;123:774–82. - PubMed
-
- Pfahler SM, Brandford A, Glaser BM. A Prospective Study of In-Office Diagnostic Vitreous Sampling in Patients with Vitreo-Retinal Pathology. Retina. 2009;29:1032–5. - PubMed
-
- Symeonidis C, Diza E, Papakonstantinou E, Souliou E, Karakiulakis G, Dimitrakos SA. Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Subretinal Fluid Correlates with the extent of Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007;245:560–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
