Role of CT perfusion imaging in the diagnosis and treatment of vasospasm
- PMID: 22773929
- PMCID: PMC3389822
- DOI: 10.2217/iim.11.19
Role of CT perfusion imaging in the diagnosis and treatment of vasospasm
Abstract
The current role of CT perfusion (CTP) imaging in the diagnosis and treatment of vasospasm in the setting of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage is discussed in this article, with specific attention directed towards defining the terminology of vasospasm and delayed cerebral ischemia. A commonly used CTP technique in clinical practice is described. A review of the literature regarding the usefulness of CTP for the diagnosis of vasospasm and its role in guiding treatment are discussed. Recent research advances in the utilization of CTP and associated ongoing challenges are also presented.
Figures
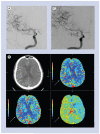
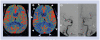
References
-
- Bederson JB, Connolly ES, Jr, Batjer HH, et al. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a statement for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the Stroke Council, American Heart Association. Stroke. 2009;40(3):994–1025. - PubMed
-
- Ingall T, Asplund K, Mahonen M, et al. A multinational comparison of subarachnoid hemorrhage epidemiology in the WHO MONICA stroke study. Stroke. 2000;31(5):1054–1061. - PubMed
-
- van Gijn J, Kerr RS, Rinkel GJ. Subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet. 2007;369(9558):306–318. - PubMed
-
- Sanelli PC, Ougorets I, Johnson CE, et al. Using CT in the diagnosis and management of patients with cerebral vasospasm. Semin. Ultrasound CT MR. 2006;27(3):194–206. - PubMed
-
-
Rosenwasser RH, Armonda RA, Thomas JE, et al. Therapeutic modalities for the management of cerebral vasospasm: timing of endovascular options. Neurosurgery. 1999;44(5):975–979. ▪ Discusses the timing of endovascular intervention in the treatment of vasospasm. The authors conclude that when a patient develops symptomatic vasospasm and is unresponsive to traditional measures of critical care management, angioplasty may be effective in improving the patient’s neurological status if this procedure is performed as early as possible. The results in this study indicate that a 2-h window may exist for restoration of blood flow to ultimately improve the patient’s outcome.
-
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
