Urocortin 3 elevates cytosolic calcium in nucleus ambiguus neurons
- PMID: 22774996
- PMCID: PMC3433571
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07869.x
Urocortin 3 elevates cytosolic calcium in nucleus ambiguus neurons
Abstract
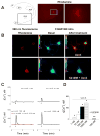
Urocortin 3 (also known as stresscopin) is an endogenous ligand for the corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 2 (CRF(2)). Despite predominant G(s) coupling of CRF(2), promiscuous coupling with other G proteins has been also associated with the activation of this receptor. As urocortin 3 has been involved in central cardiovascular regulation at hypothalamic and medullary sites, we examined its cellular effects on cardiac vagal neurons of nucleus ambiguus, a key area for the autonomic control of heart rate. Urocortin 3 (1 nM-1000 nM) induced a concentration-dependent increase in cytosolic Ca(2+) concentration that was blocked by the CRF(2) antagonist K41498. In the case of two consecutive treatments with urocortin 3, the second urocortin 3-induced Ca(2+) response was reduced, indicating receptor desensitization. The effect of urocortin 3 was abolished by pre-treatment with pertussis toxin and by inhibition of phospolipase C with U-73122. Urocortin 3 activated Ca(2+) influx via voltage-gated P/Q-type channels as well as Ca(2+) release from endoplasmic reticulum. Urocortin 3 promoted Ca(2+) release via inositol 1,4,5 trisphosphate receptors, but not ryanodine receptors. Our results indicate a novel Ca(2+) -mobilizing effect of urocortin 3 in vagal pre-ganglionic neurons of nucleus ambiguus, providing a cellular mechanism for a previously reported role for this peptide in parasympathetic cardiac regulation.
© 2012 The Authors. Journal of Neurochemistry © 2012 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests.
Figures
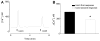
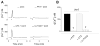
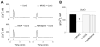
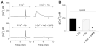
References
-
- Bale TL, Vale WW. CRF and CRF receptors: role in stress responsivity and other behaviors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004;44:525–557. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ. Neuronal calcium signaling. Neuron. 1998;21:13–26. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ. The endoplasmic reticulum: a multifunctional signaling organelle. Cell Calcium. 2002;32:235–249. - PubMed
-
- Blank T, Nijholt I, Grammatopoulos DK, Randeva HS, Hillhouse EW, Spiess J. Corticotropin-releasing factor receptors couple to multiple G-proteins to activate diverse intracellular signaling pathways in mouse hippocampus: role in neuronal excitability and associative learning. J Neurosci. 2003;23:700–707. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bouairi E, Kamendi H, Wang X, Gorini C, Mendelowitz D. Multiple types of GABAA receptors mediate inhibition in brain stem parasympathetic cardiac neurons in the nucleus ambiguus. J Neurophysiol. 2006;96:3266–3272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

