Recombinant rabbit leukemia inhibitory factor and rabbit embryonic fibroblasts support the derivation and maintenance of rabbit embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 22775411
- PMCID: PMC3411342
- DOI: 10.1089/cell.2012.0001
Recombinant rabbit leukemia inhibitory factor and rabbit embryonic fibroblasts support the derivation and maintenance of rabbit embryonic stem cells
Abstract
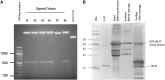
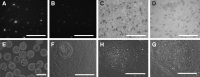
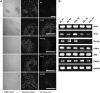
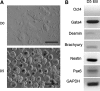
The rabbit is a classical experimental animal species. A major limitation in using rabbits for biomedical research is the lack of germ-line-competent rabbit embryonic stem cells (rbESCs). We hypothesized that the use of homologous feeder cells and recombinant rabbit leukemia inhibitory factor (rbLIF) might improve the chance in deriving germ-line-competent rbES cells. In the present study, we established rabbit embryonic fibroblast (REF) feeder layers and synthesized recombinant rbLIF. We derived a total of seven putative rbESC lines, of which two lines (M5 and M23) were from culture Condition I using mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) as feeders supplemented with human LIF (hLIF) (MEF+hLIF). Another five lines (R4, R9, R15, R21, and R31) were derived from Condition II using REFs as feeder cells supplemented with rbLIF (REF+rbLIF). Similar derivation efficiency was observed between these two conditions (8.7% vs. 10.2%). In a separate experiment with 2×3 factorial design, we examined the effects of feeder cells (MEF vs. REF) and LIFs (mLIF, hLIF vs. rbLIF) on rbESC culture. Both Conditions I and II supported satisfactory rbESC culture, with similar or better population doubling time and colony-forming efficiency than other combinations of feeder cells with LIFs. Rabbit ESCs derived and maintained on both conditions displayed typical ESC characteristics, including ESC pluripotency marker expression (AP, Oct4, Sox2, Nanog, and SSEA4) and gene expression (Oct4, Sox2, Nanog, c-Myc, Klf4, and Dppa5), and the capacity to differentiate into three primary germ layers in vitro. The present work is the first attempt to establish rbESC lines using homologous feeder cells and recombinant rbLIF, by which the rbESCs were derived and maintained normally. These cell lines are unique resources and may facilitate the derivation of germ-line-competent rbESCs.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Human foreskin fibroblast produces interleukin-6 to support derivation and self-renewal of mouse embryonic stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012 Jul 31;3(4):29. doi: 10.1186/scrt120. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 22849865 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of embryonic stem cell lines derived from New Zealand white rabbit embryos.Cloning Stem Cells. 2009 Mar;11(1):27-38. doi: 10.1089/clo.2008.0040. Cloning Stem Cells. 2009. PMID: 19220131
-
A human endothelial cell feeder system that efficiently supports the undifferentiated growth of mouse embryonic stem cells.Differentiation. 2008 Nov;76(9):923-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.2008.00280.x. Epub 2008 Jun 13. Differentiation. 2008. PMID: 18557766
-
Derivation of Human Skin Fibroblast Lines for Feeder Cells of Human Embryonic Stem Cells.Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol. 2016 Feb 3;36:1C.7.1-1C.7.11. doi: 10.1002/9780470151808.sc01c07s36. Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26840224 Review.
-
Uncovering the true identity of naïve pluripotent stem cells.Trends Cell Biol. 2013 Sep;23(9):442-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.04.004. Epub 2013 May 17. Trends Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23685019 Review.
Cited by
-
High-level expression of a novel recombinant human plasminogen activator (rhPA) in the milk of transgenic rabbits and its thrombolytic bioactivity in vitro.Mol Biol Rep. 2016 Aug;43(8):775-83. doi: 10.1007/s11033-016-4020-0. Epub 2016 May 26. Mol Biol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27230577
-
Genome engineering technologies in rabbits.J Biomed Res. 2020 Jun 12;35(2):135-147. doi: 10.7555/JBR.34.20190133. J Biomed Res. 2020. PMID: 32934190 Free PMC article.
-
Deriving rabbit embryonic stem cells by small molecule inhibitors.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Aug 15;11(8):5122-5133. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31497228 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis lesions in rabbits with deficiency of low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) on exon 7.EBioMedicine. 2018 Oct;36:29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.09.020. Epub 2018 Sep 19. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 30243490 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) during the early stage of optic nerve regeneration in zebrafish.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 27;9(8):e106010. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106010. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25162623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amit M. Carpenter M.K. Inokuma M.S. Chiu C.P. Harris C.P. Waknitz M.A. Itskovitz-Eldor J. Thomson J.A. Clonally derived human embryonic stem cell lines maintain pluripotency and proliferative potential for prolonged periods of culture. Dev. Biol. 2000;227:271–278. - PubMed
-
- Anand T. Kumar D. Singh M.K. Shah R.A. Chauhan M.S. Manik R.S. Singla S.K. Palta P. Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) embryonic stem cell-like cells and preimplantation embryos exhibit comparable expression of pluripotency-related antigens. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2011;46:50–58. - PubMed
-
- Buehr M. Meek S. Blair K. Yang J. Ure J. Silva J. McLay R. Hall J. Ying Q.L. Smith A. Capture of authentic embryonic stem cells from rat blastocysts. Cell. 2008;135:1287–1298. - PubMed
-
- Chen T.L. Shen W.J. Qiu X.W. Li T. Hoffman A.R. Kraemer F.B. Generation of novel adipocyte monolayer cultures from embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2007;16:371–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

