Generalization through the recurrent interaction of episodic memories: a model of the hippocampal system
- PMID: 22775499
- PMCID: PMC3444305
- DOI: 10.1037/a0028681
Generalization through the recurrent interaction of episodic memories: a model of the hippocampal system
Abstract
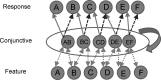
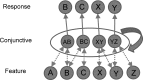
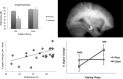
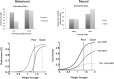
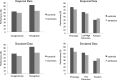
In this article, we present a perspective on the role of the hippocampal system in generalization, instantiated in a computational model called REMERGE (recurrency and episodic memory results in generalization). We expose a fundamental, but neglected, tension between prevailing computational theories that emphasize the function of the hippocampus in pattern separation (Marr, 1971; McClelland, McNaughton, & O'Reilly, 1995), and empirical support for its role in generalization and flexible relational memory (Cohen & Eichenbaum, 1993; Eichenbaum, 1999). Our account provides a means by which to resolve this conflict, by demonstrating that the basic representational scheme envisioned by complementary learning systems theory (McClelland et al., 1995), which relies upon orthogonalized codes in the hippocampus, is compatible with efficient generalization-as long as there is recurrence rather than unidirectional flow within the hippocampal circuit or, more widely, between the hippocampus and neocortex. We propose that recurrent similarity computation, a process that facilitates the discovery of higher-order relationships between a set of related experiences, expands the scope of classical exemplar-based models of memory (e.g., Nosofsky, 1984) and allows the hippocampus to support generalization through interactions that unfold within a dynamically created memory space.
Copyright 2012 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures
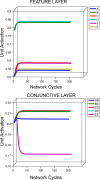
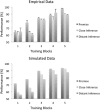
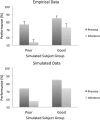
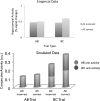
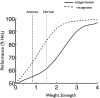

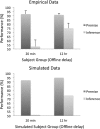
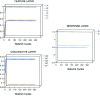
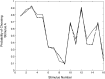
References
-
- Amaral D. G., & Lavenex P. (2006). Hippocampal neuroanatomy. In Bliss T., Andersen P., Amaral D. G., Morris R. G., & O'Keefe J. (Eds.), The hippocampus book (pp. 37–115). Oxford, England: Oxford University Press.
-
- Ashby F. G., & Maddox W. T. (2005). Human category learning. Annual Review of Psychology, 56, 149–178. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.56.091103.070217 - PubMed
-
- Bartlett F. C. (1932). Remembering: An experimental and social study. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
-
- Becker S. (2005). A computational principle for hippocampal learning and neurogenesis. Hippocampus, 15, 722–738. doi:10.1002/hipo.20095 - PubMed
-
- Bowers J. S. (2009). On the biological plausibility of grandmother cells: Implications for neural network theories in psychology and neuroscience. Psychological Review, 116, 220–251. doi:10.1037/a0014462 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

