The Aastrom experience
- PMID: 22776246
- PMCID: PMC3580464
- DOI: 10.1186/scrt117
The Aastrom experience
Abstract
Aastrom Biosciences has developed a proprietary cell-processing technology that enables the manufacture of ixmyelocel-T, a patient-specific multicellular therapy expanded from a small sample of a patient's own bone marrow. Ixmyelocel-T is produced under current good manufacturing practices (cGMP) in a fully closed, automated system that expands mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and macrophages. While the cell types in ixmyelocel-T are the same as those found in the bone marrow, the numbers of MSCs and alternative macrophages are greater in ixmyelocel-T. We propose that the mixture of expanded MSCs and alternatively activated macrophages promote long-term tissue repair of ischemic tissue. The multiple cell types in ixmyelocel-T have a range of biological activities that are likely to contribute to a complex mechanism of action. Clinical trial data collected to date support the potential for ixmyelocel-T as an efficacious and safe treatment for ischemic cardiovascular indications, including critical limb ischemia (CLI) and a severe form of heart failure, dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). The CLI clinical program has completed phase 2 and has reached concurrence with the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on a phase 3 study (REVIVE) through the Special Protocol Assessment (SPA) process. The phase 3 study began screening patients in February 2012. The DCM clinical program will initiate phase 2b in 2012.
Figures

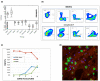

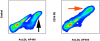




References
-
- Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhjan RK, Lalykina KS. The development of fibroblast colonies in monolayer cultures of guinea-pig bone marrow and spleen cells. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1970;3:393–403. - PubMed
-
- National Institutes of Health. The Adult Stem Cell (Stem Cell Information) http://stemcells.nih.gov/info/scireport/chapter4
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

