Induction of anti-Ro60/anti-La by immunisation with spectrin and induction of anti-spectrin by immunisation with Ro60 and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-modified Ro60 immunisation
- PMID: 22776429
- PMCID: PMC5664947
Induction of anti-Ro60/anti-La by immunisation with spectrin and induction of anti-spectrin by immunisation with Ro60 and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-modified Ro60 immunisation
Abstract
Objectives: The Ro ribonucleoprotein particle, targeted in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and Sjögren's syndrome (SS), includes Ro60 (SSA) and La (SSA) autoantigens. Anti-Ro60 occurs in SLE and SS. The importance of α-fodrin and spectrin as well as anti-Ro and anti-fodrin/spectrin antibodies in SS and SLE, led us to hypothesise that rabbit immunisation with Ro60 or 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-modified Ro60 would induce anti-spectrin. In addition, we hypothesised that antibodies to Ro60 and La will develop in animals immunised with spectrin.
Methods: Two NZW rabbits each were immunised with 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-modified Ro60 or unmodified Ro60. Methods used included ELISA, including an inside-out RBC membrane ELISA, and Crithidia lucilae assays.
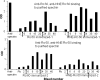
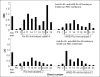
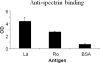
Results: Commercial anti-spectrin sera bound significantly to Ro60 (OD 2.6 ± 0.1), Ro60 multiple antigenic peptides (MAPs) (3 out of 21 Ro60 MAPs), La (OD 4.4±0.5), and La fragments as well as to double stranded DNA but not to BSA (OD 0.6±0.1). Anti-spectrin binding to purified spectrin could be inhibited by spectrin (>95%), and Ro60 or La (70%). When the binding of anti-spectrin was tested against a nested set of La fragments we found that a N4 fragment representing the C-terminal 250 aa (aa 159 to 408) bound the strongest (OD=4.12) followed by a N9 fragment (the C-terminal 36aa; aa373 to 408 (OD=1.36). Also, significant anti-spectrin antibody levels were induced by Ro60 and HNE-modified Ro60 immunisation.
Conclusions: We found intermolecular epitope spreading from Ro60/La to spectrin and vice versa, and this may have pathological significance in these animal models of autoimmunity.
Figures



References
-
- Harley JB, Yamagata H, Reichlin M. Anti-La/SSB antibody is present in some normals and is coincident with anti-Ro/SSA precipitins in systemic lupus erythematosus. Journal of Rheumatology. 1984;11:309–14. - PubMed
-
- Harley JB, Scofield RH, Reichlin M. Anti-Ro in Sjögren’s syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America. 1992;18:337–58. - PubMed
-
- Harley JB, Sestak AS, Willis LG, Fu SM, Hansen JA, Reichlin M. A model for disease heterogeneity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Relationships between histocompatibility antigens, autoantibodies and lymphopenia or renal disease. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 1989;32:826–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
