Genome-wide analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in soybean
- PMID: 22776508
- PMCID: PMC3462118
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-106
Genome-wide analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in soybean
Abstract
Background: The MYB superfamily constitutes one of the most abundant groups of transcription factors described in plants. Nevertheless, their functions appear to be highly diverse and remain rather unclear. To date, no genome-wide characterization of this gene family has been conducted in a legume species. Here we report the first genome-wide analysis of the whole MYB superfamily in a legume species, soybean (Glycine max), including the gene structures, phylogeny, chromosome locations, conserved motifs, and expression patterns, as well as a comparative genomic analysis with Arabidopsis.
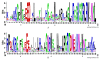
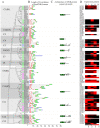
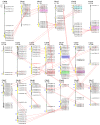
Results: A total of 244 R2R3-MYB genes were identified and further classified into 48 subfamilies based on a phylogenetic comparative analysis with their putative orthologs, showed both gene loss and duplication events. The phylogenetic analysis showed that most characterized MYB genes with similar functions are clustered in the same subfamily, together with the identification of orthologs by synteny analysis, functional conservation among subgroups of MYB genes was strongly indicated. The phylogenetic relationships of each subgroup of MYB genes were well supported by the highly conserved intron/exon structures and motifs outside the MYB domain. Synonymous nucleotide substitution (dN/dS) analysis showed that the soybean MYB DNA-binding domain is under strong negative selection. The chromosome distribution pattern strongly indicated that genome-wide segmental and tandem duplication contribute to the expansion of soybean MYB genes. In addition, we found that ~ 4% of soybean R2R3-MYB genes had undergone alternative splicing events, producing a variety of transcripts from a single gene, which illustrated the extremely high complexity of transcriptome regulation. Comparative expression profile analysis of R2R3-MYB genes in soybean and Arabidopsis revealed that MYB genes play conserved and various roles in plants, which is indicative of a divergence in function.
Conclusions: In this study we identified the largest MYB gene family in plants known to date. Our findings indicate that members of this large gene family may be involved in different plant biological processes, some of which may be potentially involved in legume-specific nodulation. Our comparative genomics analysis provides a solid foundation for future functional dissection of this family gene.
Figures

References
-
- Riechmann JL, Heard J, Martin G, Reuber L, Jiang C, Keddie J, Adam L, Pineda O, Ratcliffe OJ, Samaha RR, Creelman R, Pilgrim M, Broun P, Zhang JZ, Ghandehari D, Sherman BK, Yu G. Arabidopsis transcription factors: genome–wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science. 2000;290:2105–2110. doi: 10.1126/science.290.5499.2105. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amoutzias GD, Veron AS, Weiner J 3rd, Robinson-Rechavi M, Bornberg-Bauer E, Oliver SG, Robertson DL. One billion years of bZIP transcription factor evolution: conservation and change in dimerization and DNA-binding site specificity. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24:827–835. - PubMed
-
- Lipsick JS. One billion years of Myb. Oncogene. 1996;13:223–235. - PubMed
-
- Stracke R, Werber M, Weisshaar B. The R2R3–MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Opin Plant Bio. 2001;l4:447–456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

