Carotid inflammation is unaltered by exercise in hypercholesterolemic Swine
- PMID: 22776877
- PMCID: PMC4671366
- DOI: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e318266af0a
Carotid inflammation is unaltered by exercise in hypercholesterolemic Swine
Abstract
Introduction: Reduction of vascular inflammation might contribute to the beneficial effects of exercise. We hypothesized that 1) exercise would reduce carotid endothelial vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and that 2) in vivo detection of carotid inflammation can be achieved in a large animal model using contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEU) with VCAM-1-targeted microbubbles (MBs).
Methods: Familial hypercholesterolemic (FH) swine were divided into sedentary (Sed) and exercise-trained (Ex) groups. Ex pigs underwent 16-20 wk of treadmill aerobic exercise. At the end of the study, in vivo CEU with VCAM-1-targeted MBs and assessment of endothelial-dependent dilation (EDD) were performed in carotid arteries. VCAM-1 mRNA and protein expression were compared with markers of atherosclerotic disease and health, and in vitro EDD was assessed in carotid arteries.
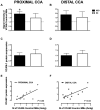
Results: Exercise training neither reduced inflammation nor improved EDD in carotid arteries of FH swine. Markers of atherosclerosis including VCAM-1 were prominent in the bifurcation compared with the proximal or distal common carotid artery and inversely associated with phosphorylated and total endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Signal intensity from VCAM-1-to-control MBs positively correlated with carotid VCAM-1 protein expression, validating our technique.
Conclusion: These results first demonstrate that aerobic exercise has no effect on carotid endothelial inflammatory markers and EDD in FH swine. Second, our findings indicate that CEU using VCAM-1-targeted MBs can detect inflammation in vivo, providing strong foundations for longitudinal studies examining the effect of therapeutic interventions on the inflammatory status of the endothelium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest pertaining to this work. The results of the present study do not constitute and endorsement by ACSM.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Exercise training and vascular cell phenotype in a swine model of familial hypercholesterolaemia: conduit arteries and veins.Exp Physiol. 2014 Feb;99(2):454-65. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2013.075838. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Exp Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24213857 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular imaging of inflammation in atherosclerosis with targeted ultrasound detection of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1.Circulation. 2007 Jul 17;116(3):276-84. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.684738. Epub 2007 Jun 25. Circulation. 2007. PMID: 17592078
-
Endurance exercise training improves endothelium-dependent relaxation in brachial arteries from hypercholesterolemic male pigs.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2005 Oct;99(4):1412-21. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00293.2005. Epub 2005 Jun 23. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2005. PMID: 15976363
-
Endothelium-mediated control of coronary vascular tone after chronic exercise training.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1995 Aug;27(8):1135-44. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1995. PMID: 7476057 Review.
-
Molecular imaging of carotid plaque vulnerability.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015;39(1):5-12. doi: 10.1159/000369123. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 25547782 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound Molecular Imaging of Inflammation in Mouse Abdominal Aorta.Invest Radiol. 2017 Sep;52(9):499-506. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000373. Invest Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28430714 Free PMC article.
-
Microvascular insulin resistance in skeletal muscle and brain occurs early in the development of juvenile obesity in pigs.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018 Feb 1;314(2):R252-R264. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00213.2017. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29141949 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound molecular imaging: Moving toward clinical translation.Eur J Radiol. 2015 Sep;84(9):1685-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.03.016. Epub 2015 Mar 21. Eur J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25851932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endurance exercise training does not limit coronary atherosclerosis in familial hypercholesterolemic swine.Physiol Rep. 2019 Feb;7(4):e14008. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14008. Physiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30809955 Free PMC article.
-
Optical Verification of Microbubble Response to Acoustic Radiation Force in Large Vessels With In Vivo Results.Invest Radiol. 2015 Nov;50(11):772-84. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000185. Invest Radiol. 2015. PMID: 26135018 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnett HJ, Gunton RW, Eliasziw M, Fleming L, Sharpe B, Gates P, Meldrum H. Causes and severity of ischemic stroke in patients with internal carotid artery stenosis. JAMA: the journal of the American Medical Association. 2000;283 (11):1429–1436. - PubMed
-
- Belardinelli R, Georgiou D, Cianci G, Purcaro A. Randomized, controlled trial of long-term moderate exercise training in chronic heart failure: effects on functional capacity, quality of life, and clinical outcome. Circulation. 1999;99 (9):1173–1182. - PubMed
-
- Bonomini F, Tengattini S, Fabiano A, Bianchi R, Rezzani R. Atherosclerosis and oxidative stress. Histol Histopathol. 2008;23 (3):381–390. - PubMed
-
- Bots ML, Baldassarre D, Simon A, de Groot E, O’Leary DH, Riley W, Kastelein JJ, Grobbee DE. Carotid intima-media thickness and coronary atherosclerosis: weak or strong relations? Eur Heart J. 2007;28 (4):398–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

