Multiple roles for the Ess1 prolyl isomerase in the RNA polymerase II transcription cycle
- PMID: 22778132
- PMCID: PMC3422015
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00672-12
Multiple roles for the Ess1 prolyl isomerase in the RNA polymerase II transcription cycle
Abstract
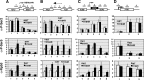
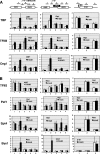
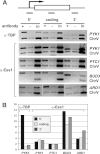
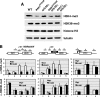
The Ess1 prolyl isomerase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae regulates RNA polymerase II (pol II) by isomerizing peptide bonds within the pol II carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) heptapeptide repeat (YSPTSPS). Ess1 preferentially targets the Ser5-Pro6 bond when Ser5 is phosphorylated. Conformational changes in the CTD induced by Ess1 control the recruitment of essential cofactors to the pol II complex and may facilitate the ordered transition between initiation, elongation, termination, and RNA processing. Here, we show that Ess1 associates with the phospho-Ser5 form of polymerase in vivo, is present along the entire length of coding genes, and is critical for regulating the phosphorylation of Ser7 within the CTD. In addition, Ess1 represses the initiation of cryptic unstable transcripts (CUTs) and is required for efficient termination of mRNA transcription. Analysis using strains lacking nonsense-mediated decay suggests that as many as half of all yeast genes depend on Ess1 for efficient termination. Finally, we show that Ess1 is required for trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4). Thus, Ess1 has direct effects on RNA polymerase transcription by controlling cofactor binding via conformationally induced changes in the CTD and indirect effects by influencing chromatin modification.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Ess1 prolyl isomerase: traffic cop of the RNA polymerase II transcription cycle.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1839(4):316-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.02.001. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24530645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional interaction of the Ess1 prolyl isomerase with components of the RNA polymerase II initiation and termination machineries.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Jun;29(11):2925-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01655-08. Epub 2009 Mar 30. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19332564 Free PMC article.
-
The ESS1 prolyl isomerase and its suppressor BYE1 interact with RNA pol II to inhibit transcription elongation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2003 Dec;165(4):1687-702. doi: 10.1093/genetics/165.4.1687. Genetics. 2003. PMID: 14704159 Free PMC article.
-
The Ess1 prolyl isomerase is required for transcription termination of small noncoding RNAs via the Nrd1 pathway.Mol Cell. 2009 Oct 23;36(2):255-66. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.08.018. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19854134 Free PMC article.
-
The CTD code of RNA polymerase II: a structural view.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013 Jan-Feb;4(1):1-16. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1138. Epub 2012 Oct 5. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013. PMID: 23042580 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure analysis suggests Ess1 isomerizes the carboxy-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II via a bivalent anchoring mechanism.Commun Biol. 2021 Mar 25;4(1):398. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01906-8. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33767358 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary and Structural Insights into the RNA Polymerase I A34 Protein Family: A Focus on Intrinsic Disorder and Phase Separation.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jan 7;16(1):61. doi: 10.3390/genes16010061. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858608 Free PMC article.
-
A Conserved Nuclear Cyclophilin Is Required for Both RNA Polymerase II Elongation and Co-transcriptional Splicing in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2016 Aug 19;12(8):e1006227. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006227. eCollection 2016 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27541139 Free PMC article.
-
The Ess1 prolyl isomerase: traffic cop of the RNA polymerase II transcription cycle.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1839(4):316-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.02.001. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24530645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interrogation of the cell wall integrity pathway in Aspergillus niger identifies a putative negative regulator of transcription involved in chitin deposition.Gene X. 2020 Jan 28;5:100028. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.100028. eCollection 2020 Dec. Gene X. 2020. PMID: 32550555 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
