Nocardiosis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis treated with rituximab and a summary of reported cases
- PMID: 22778377
- PMCID: PMC3029947
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr.11.2009.2421
Nocardiosis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis treated with rituximab and a summary of reported cases
Abstract
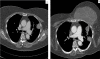
Rituximab is a B-cell-depleting monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody. It is widely used in haematology and rheumatology. However, usage of rituximab in immunosupressed patient has been associated with various opportunistic infections. The authors reported a case of refractory rheumatoid arthritis treated with rituximab, which later presented with non-resolving pneumonia with pulmonary nodule. Percutaneous computer tomogram guided lung biopsy was arranged to confirm the suspicion of tuberculosis, but did not yield conclusive results. Later, she presented left-chest abscess and underwent incision and drainage. The pus culture and sensitivity confirmed pulmonary nocardiosis with chest wall dissemination. She was treated with 2-week course of trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole and responded. The authors also reviewed published cases of nocardiosis post-rituximab.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nocardia transvalensis infection in an immunocompetent patient reported from Turkey.Tuberk Toraks. 2007;55(3):295-8. Tuberk Toraks. 2007. PMID: 17978929
-
Pulmonary nocardiosis in human immunodeficiency virus infection: a tuberculosis mimic.J Postgrad Med. 2001 Jan-Mar;47(1):30-2. J Postgrad Med. 2001. PMID: 11590288
-
Rituximab seems to be a safer alternative in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with tuberculosis.BMJ Case Rep. 2013 Jan 21;2013:bcr2012006585. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2012-006585. BMJ Case Rep. 2013. PMID: 23341582 Free PMC article.
-
Induced psoriasis after rituximab therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: a case report and review of the literature.Rheumatol Int. 2013 Nov;33(11):2927-30. doi: 10.1007/s00296-012-2581-3. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Rheumatol Int. 2013. PMID: 23135613 Review.
-
Myocardial infarction after rituximab treatment for rheumatoid arthritis: Is there a link?Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(4):496-9. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990386. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 23565629 Review.
References
-
- Cohen SB, Emery P, Greenwald MW, et al. ; REFLEX Trial Group Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: Results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:2793–806 - PubMed
-
- Martínez R, Reyes S, Menéndez R. Pulmonary nocardiosis: risk factors, clinical features, diagnosis and prognosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2008;14:219–27 - PubMed
-
- Lederman ER, Crum NF. A case series and focused review of nocardiosis: clinical and microbiologic aspects. Medicine 2004;83:300–13 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical