Adiponectin is critical in determining susceptibility to depressive behaviors and has antidepressant-like activity
- PMID: 22778410
- PMCID: PMC3409774
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1202835109
Adiponectin is critical in determining susceptibility to depressive behaviors and has antidepressant-like activity
Abstract
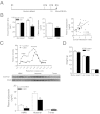
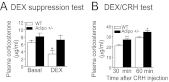
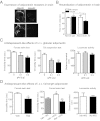
Depression is a debilitating mental illness and is often comorbid with metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes. Adiponectin is an adipocyte-derived hormone with antidiabetic and insulin-sensitizing properties. Here we show that adiponectin levels in plasma are reduced in a chronic social-defeat stress model of depression, which correlates with decreased social interaction time. A reduction in adiponectin levels caused by haploinsufficiency results in increased susceptibility to social aversion, "anhedonia," and learned helplessness and causes impaired glucocorticoid-mediated negative feedback on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. Intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) injection of an adiponectin neutralizing antibody precipitates stress-induced depressive-like behavior. Conversely, i.c.v. administration of exogenous adiponectin produces antidepressant-like behavioral effects in normal-weight mice and in diet-induced obese diabetic mice. Taken together, these results suggest a critical role of adiponectin in depressive-like behaviors and point to a potential innovative therapeutic approach for depressive disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ali S, Stone MA, Peters JL, Davies MJ, Khunti K. The prevalence of co-morbid depression in adults with Type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabet Med. 2006;23:1165–1173. - PubMed
-
- Knol MJ, et al. Depression as a risk factor for the onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus. A meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2006;49:837–845. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RJ, Freedland KE, Clouse RE, Lustman PJ. The prevalence of comorbid depression in adults with diabetes: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:1069–1078. - PubMed
-
- Andersohn F, Schade R, Suissa S, Garbe E. Long-term use of antidepressants for depressive disorders and the risk of diabetes mellitus. Am J Psychiatry. 2009;166:591–598. - PubMed
-
- Brown LC, Majumdar SR, Johnson JA. Type of antidepressant therapy and risk of type 2 diabetes in people with depression. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008;79:61–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

