Unusual association of Arnold-Chiari malformation and vitamin B12 deficiency
- PMID: 22778461
- PMCID: PMC4543072
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-03-2012-6138
Unusual association of Arnold-Chiari malformation and vitamin B12 deficiency
Abstract
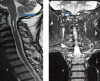
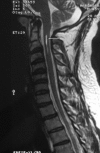
Arnold-Chiari malformations are a group of congenital or acquired defects associated with the displacement of cerebellar tonsils into the spinal canal. First described by Chiari (1891), this has various grades of severity and involves various parts of neuraxis, for example, cerebellum and its outputs, neuro-otological system, lower cranial nerves, spinal sensory and motor pathways. The symptomatology of Arnold-Chiari malformations may mimic multiple sclerosis, primary headache syndromes, spinal tumours and benign intracranial hypertension. We highlighted a case of Chiari type I malformation, who presented with posterolateral ataxia associated with significant vitamin B(12) deficiency. The patient was supplemented with vitamin B(12) injections and showed remarkable improvement at follow-up after 3 months.
Figures
References
-
- Geroldi C, Frisoni GB, Bianchetti A, et al. Arnold-Chiari malformation with syringomyelia in an elderly woman. Age Ageing 1999;28:399–400. - PubMed
-
- Bejjani GK. What do tonsillar herniation and idiopathic intracranial hypertension have in common? Successful management of recurrent Chiari malformation with CSF diversion. Transactions of the 12th World Congress of Neurosurgery; Sydney, Australia: WFNS, 2001:16–21.
-
- Lindenbaum J, Healton EB, Savage DG, et al. Neuropsychiatric disorders caused by cobalamin deficiency in the absence of anemia or macrocytosis. N Engl J Med 1988;318:1720–8. - PubMed
-
- Milhorat TH, Chou MW, Trinidad EM, et al. Chiari I malformation redefined: clinical and radiographic findings for 364 symptomatic patients. Neurosurgery 1999;44:1005–17. - PubMed
-
- Menezes AH. Chiari I malformations and hydromyelia: complications. Pediatr Neurosurg 1991;17:146–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical